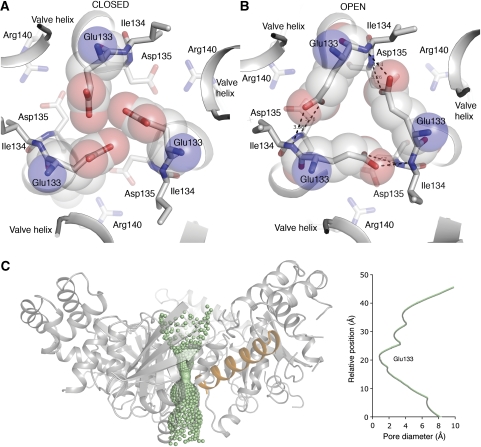
Figure 3.
Details of the cytoplasmic gate. (A) Apo structure. View from the membrane side down the centre of the trimer. The trimer is stabilized through a salt bridge formed between Asp135 and Arg140 in neighbouring protomers. In the apo state, Glu133 is pointing to the centre, effectively closing the pore. (B) In the mGTP-bound structure, structural changes leads to a shift in the position of Cα atoms surrounding the centre of the trimer. This enables Glu133 to change conformation and form hydrogen bonds with mainchain N-atoms of Ile134. The new conformation leads to opening of a central cytoplasmic pore. (C) The pore diameter along the proposed cytoplasmic gate in the open state. The main site of constriction and gating (residue Glu133) is depicted. The valve helix from one protomer is shown in orange to illustrate its position in relation to the pore. The cytoplasmic pore was generated using HOLE (Smart et al, 1993).