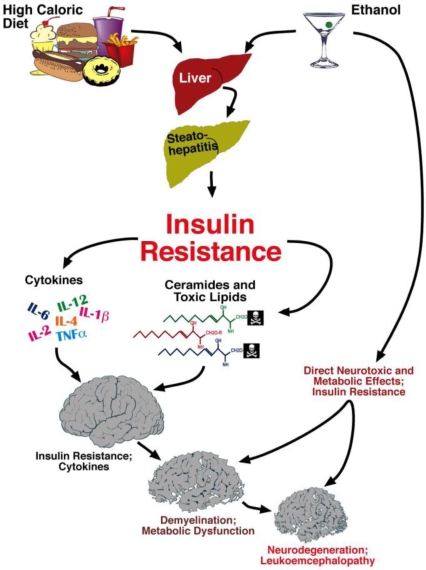
Figure 7.
Liver-brain axis of neurodegeneration—Hypothesis. Progressive hepatic steatosis incites inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokine activation. Attendant insulin resistance initiates a lipolysis and lipid disequilibrium cascade, leading to increased production and accumulation of ceramides. Ceramides are cytotoxic and promote insulin resistance, and their lipid solubility enables ready transfer across the blood-brain barrier to cause CNS insulin resistance and neurodegeneration with loss of neurons and oligodendrocytes. Ethanol’s lipid solubility enables it to exert direct neurotoxic effects, and cause brain insulin resistance.