Figure 3.
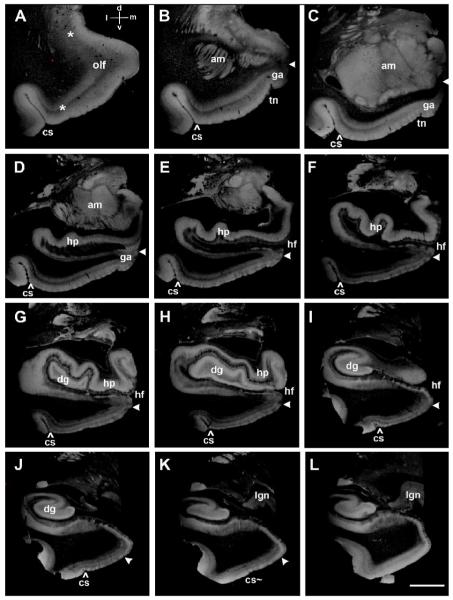
The rostrocaudal and mediolateral limits of EC in high resolution ex vivo MRI (100μm isotropic voxels). (A) Primary olfactory cortex is loosely marked with asterisks and anterior EC is between the lateral asterisk and ‘olf’ label. A coordinate system is labeled,‘d’ for dorsal, ‘v’ for ventral, ‘l’ for lateral and ‘m’ for medial in A for all panels. White arrowheads throughout figure 3 demarcate the medial entorhinal boundary while the caret (^) demarcates the lateral entorhinal limit. (B), (C) and (D) show EC at the level of gyrus ambiens (area 34) with the tentorial notch distinguishing entorhinal area 34 from entorhinal area 28. (E), (F), (G) and (H) demonstrate the ‘pes’ hippocampi at the uncal hippocampal level. (I) shows the ending of the hippocampal head and the size of the parahippocampal gyrus is becoming smaller. (J) and (K) display the posterior EC and concurrently the collateral sulcus ends (cs∼) in (K) at approximately the level of the lateral geniculate nucleus. At level (L), entorhinal islands are no longer observed. Abbreviations: am=amygdala; cs=collateral sulcus; ec=entorhinal cortex; dg=dentate gyrus; ga=gyrus ambiens; hp=hippocampus; hf=hippocampal fissure; olf=olfactory; lgn=lateral geniculate nucleus; sub=subiculum; para=parasubiculum; pre=presubiculum; pc=perirhinal cortex; tn=tentorial notch. Magnification bar=1cm.