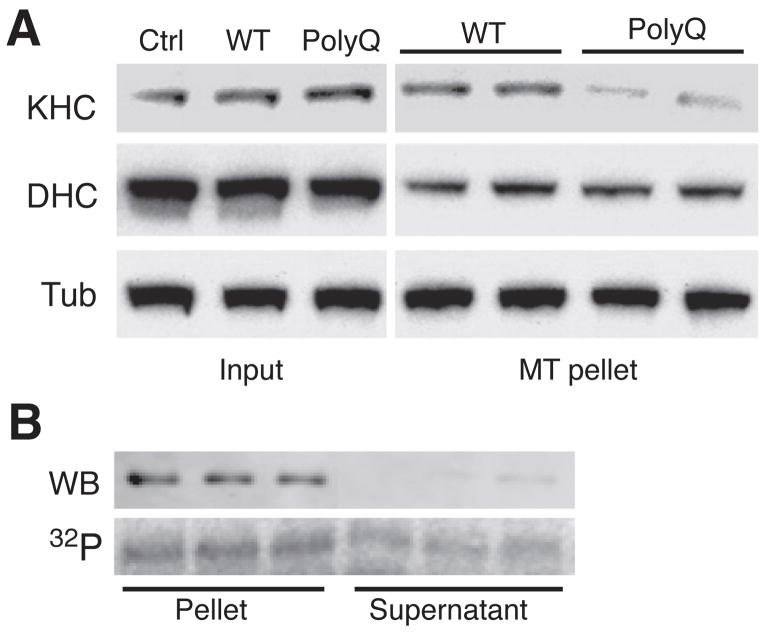
Figure 7. PolyQ-Htt expression inhibits kinesin-1 binding to microtubules.
A) Lysates of NSC34 cells transfected with WT-Htt or polyQ-Htt as in Fig. 3A were analyzed by immunoblot. Total levels (Input) of kinesin-1 (KHC), dynein heavy chain (DHC) and tubulin (Tub) were comparable for untransfected (Ctrl), WT-Htt and polyQ-Htt-expressing cells. However, the fraction of kinesin-1 recovered in association with microtubules was reduced for lysates from polyQ-Htt expressing cells, when compared to untransfected and WT-Htt-expressing cells. B) Microtubule-binding assays using recombinant kinesin-1 (KHC584). Immunoblot (WB) shows that unphosphorylated KHC584 is mainly recovered in association with microtubules (Pellet). An autoradiogram (32P) reveals a significant fraction of JNK3-phosphorylated KHC584 remains in the supernatant.