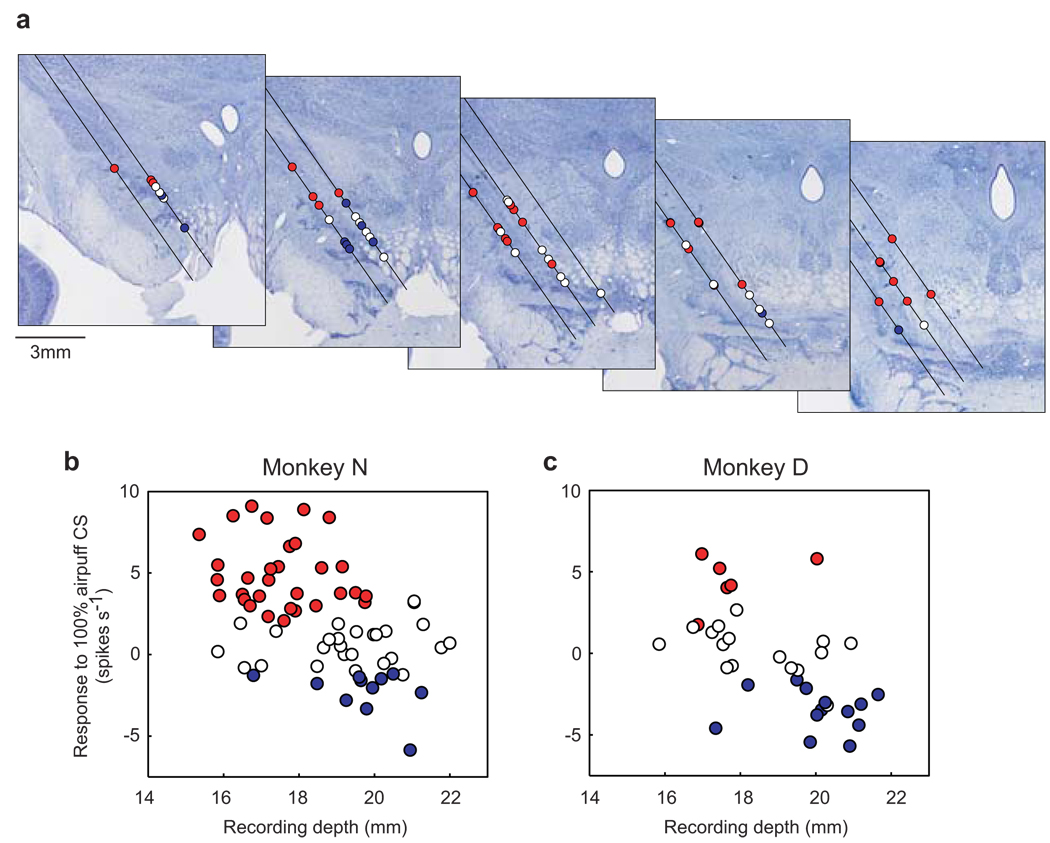
Figure 4. Locations of dopamine neurons in relation to their responses to airpuff-predicting CS.
a, Recording sites of 68 dopamine neurons in monkey N are plotted on five coronal sections shown rostrocaudally from left to right (interval: 1 mm). Red circles indicate neurons showing significant excitations to 100% airpuff CS (i.e., ACS-excited type neurons). Blue circles indicate neurons showing significant inhibitions to 100% airpuff CS (i.e., ACS-inhibited type neurons). White circles, no significance (i.e., ACS-nonresponsive type neurons). Black lines indicate electrode penetration tracks which were tilted laterally by 35 degrees. b, c, Relation between recording depth and the response to 100% airpuff CS for monkey N (b) and monkey D (c). Red, blue, and white circles indicate ACS-excited, ACS-inhibited, and ACS-nonresponsive type neurons. The recording depth was measured from a reference depth set by a manipulator to advance the recording electrode.