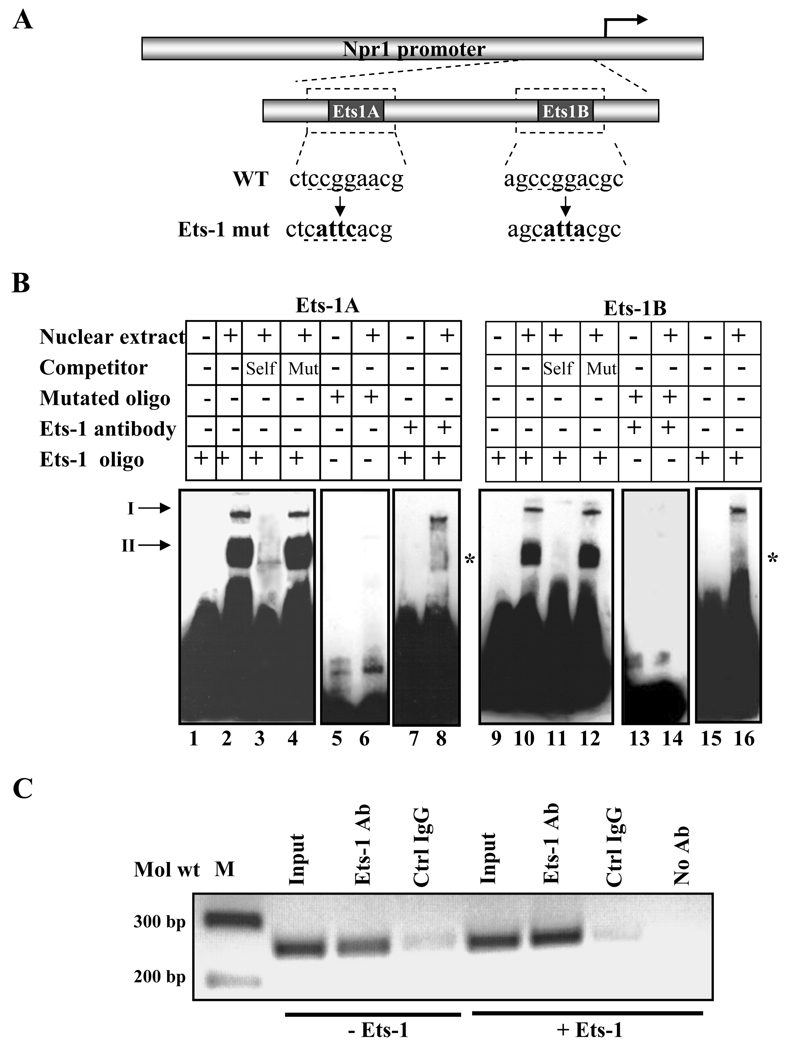
Fig. 2. In vitro and in vivo binding of Ets-1.
A) Schematic diagram showing the sequence of the wild-type and mutated Ets-1 binding site in the Npr1 promoter. WT and mut indicate the wild-type and mutant sequences, respectively, and underlined nucleotides show the mutated sequence. B) The gel retardation assay in nuclear extract from MMCs using Ets-1A and Ets-1B oligonucleotides. Lanes 2 and 10 show the nuclear protein complex binding with Ets-1A and Ets-1B sites, respectively. Unlabeled competitor DNA was used in a 200-fold molar excess concentration in Lanes 3 and 11 (wild-type Ets-1A and Ets-1B) and Lanes 4 and 12 (mutant Ets-1A and Ets-1B). In lanes 6 and 14, labeled mutant Ets-1A and Ets-1B oligonucleotides, respectively, were used for binding reactions. Ets-1 antibody was used for a supershift assay in lanes 8 and 16. Arrows I and II indicate specific DNA-protein binding complex; asterisk shows the disruption of Ets-1 nuclear protein complex binding in the presence of the antibody. C) ChIP assay of the Npr1 gene promoter in Ets-1-transfected cells. PCR amplification of the immunoprecipitated DNA shows binding of Ets-1 to the Npr1 promoter region, which contains two Ets-1 binding sites. Samples immunoprecipitated with control IgG (Crtl IgG) showed a very faint band and in the absence of antibody showed no detectable signals after PCR amplification. -Ets indicates transfection with empty vector (pEVRF0) and +Ets indicates transfection with Ets-1 expression plasmid. Representative results of three experiments are shown.