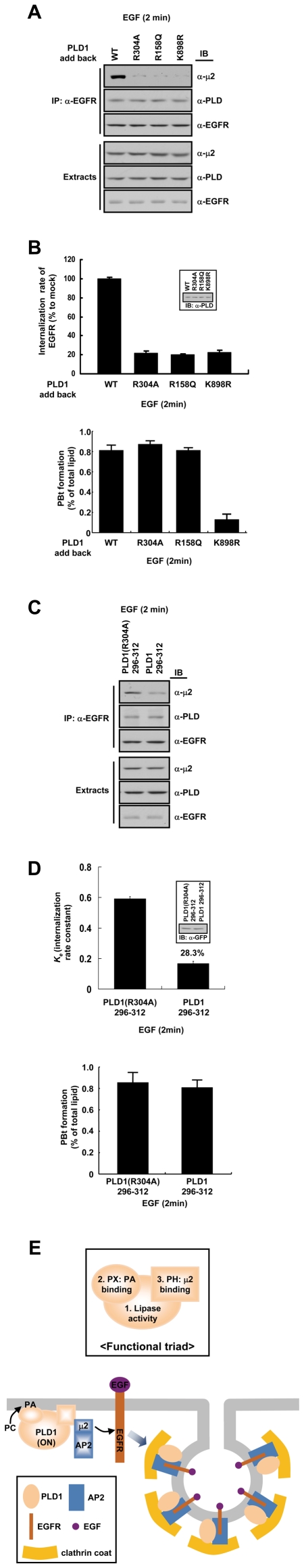
Figure 5. PLD1-μ2 interaction is important for PLD1-mediated EGFR endocytosis.
(A) The recognition of EGFR by μ2 was analyzed by western blotting. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-EGFR antibody and then immunoblotted using the indicated antibodies. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with wild type, R304A, R158Q, or K898R PLD1 after being depleted of endogenous PLD1. After 2 min of EGF (20 nM) treatment, the internalization rate of EGFR was measured as in Figure 1 (D). The PLD1 lipase activity was measured in a parallel experiment. Immunoblot in the insets indicates the expression levels of the constructs used. (C) and (D) The effect of PLD1-μ2 interaction on EGFR-μ2 association (C) and EGFR internalization rate (D) was checked. (E) Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism whereby PLD1 facilitates EGFR endocytosis in an auto-regulatory manner. Upon EGF stimulation, PLD1 is activated and generates PA. Association between PLD1 and PA through the PX domain of PLD1 increases the affinity of the interaction between the PH domain of PLD1 and μ2. This interaction enhances the translocation of AP2 onto the plasma membrane and the recognition of EGFR by μ2 facilitating EGFR endocytosis.