Fig. 2.
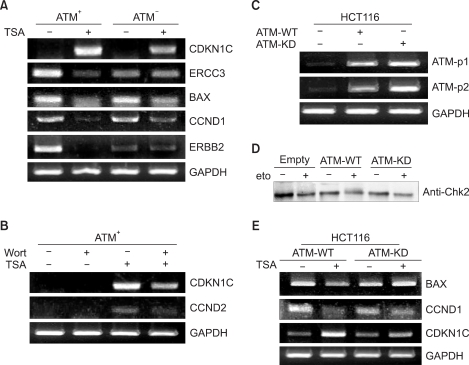
The oligonucleotide microarray results were validated by RT-PCR analysis of the expression of selected genes in the ATM- cells, the ATM+ cells and the HCT116 cells. (A) The expressions of the TSA responsive genes were evaluated by RT-PCR as being representative of the ATM-regulated genes. The TSA-induced increase in the level of CDKN1C mRNA was reduced in the absence of ATM. The TSA-induced reduction of the expressions of ERCC3, BAX, CND1 and ERBB2 mRNAs was observed in the ATM+ cells, but not the ATM- cells. (B) The effect of wortmannin on the expression of the ATM-regulated genes in response to TSA. Inhibition of ATM kinase activity by wortmannin attenuated the TSA-induced transcriptional effects on upregulation of the CDKN1C and CCND2 genes. (C) The ATM-expressing constructs were transiently transfected into HCT116 cells, and the expression levels of ATM-WT or ATM-KD were checked by RT-PCR with using the primer sets ATM-p1 (exon 7~10) and ATM-p2 (exon 10~13). (D) Monitoring of the ATM pathway activation after etoposide treatment by measuring the Chk2 phosphorylation in the HCT116 cells expressing ATM-WT or ATM-KD. In response to etoposide, ATM-WT phosphorylated Chk2 and this resulted in the shifted mobility of the phosphorylated Chk2 proteins, compared with that of nonphosphorylated Chk2. (E) Evaluation of the mRNA expression of the genes regulated by TSA in the HCT116 cells expressing ATM-WT or ATM-KD. The expressions of BAX and CCND1 were reduced in response to TSA in the cells expressing ATM-WT, and that of CDKN1C increased in the cells expressing ATM-WT. TSA-induced downregulation of BAX and CCND1 and upregulation of CDKN1C was rarely detected in the cells expressing ATM-KD. GAPDH mRNA was amplified as an internal control.