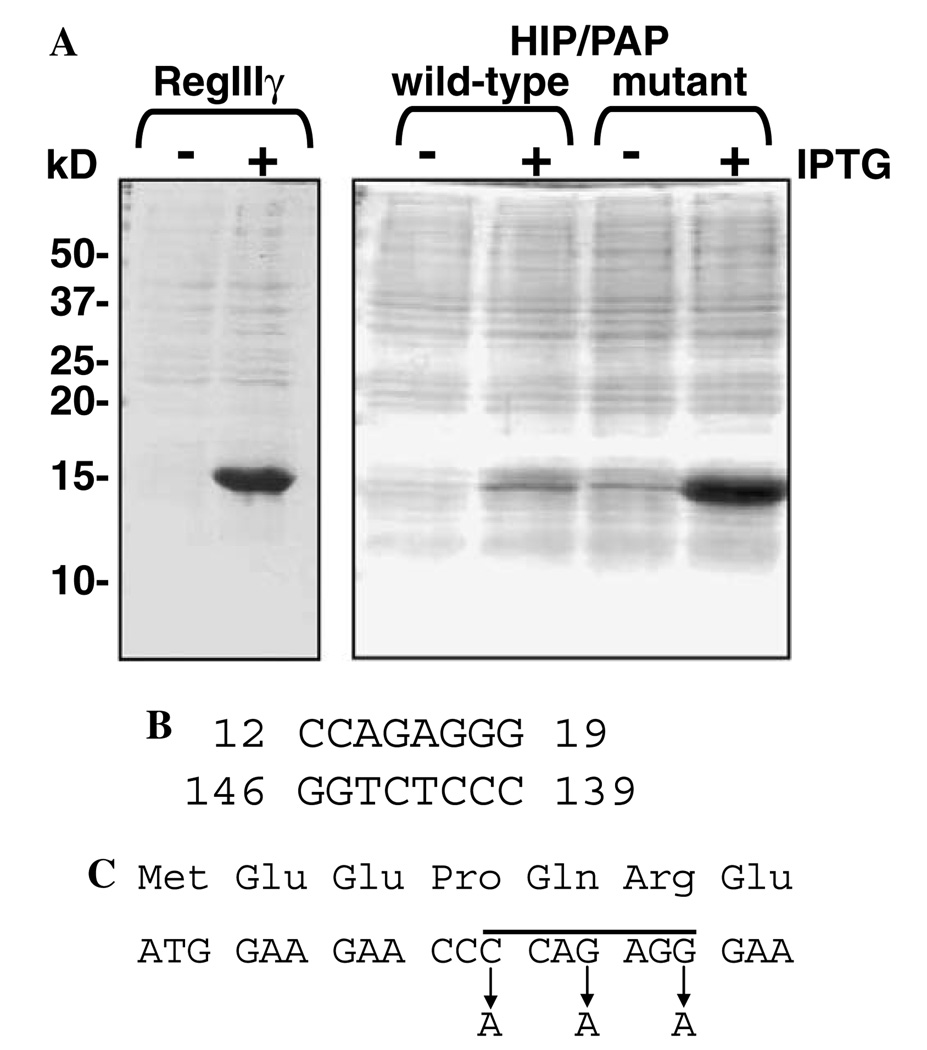
Fig. 1.
Expression of mouse RegIIIγ and human HIP/PAP in E. coli. (A) Expression of RegIIIγ (pET3a-RegIIIy) was induced by the addition of 0.4 mM IPTG. HIP/PAP expression constructs (wild-type = pET3a-HIP/PAP; mutant = pET3a-HIP/PAPmut) were induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG. Total E. coli lysates from pre- and post-induction cultures were analyzed by electrophoresis through a 15% SDS–PAGE gel followed by Coomassie blue staining. (B) Predicted stem structure involving residues 12–19 of the HIP/PAP mRNA coding region. The stem was predicted by analyzing the mature HIP/PAP coding sequence using the web-based RNA secondary structure prediction algorithm at www.gene-bee.msu.su. (C) Positions of the silent mutations incorporated into the forward primer used to generate pET3a-HIP/PAPmut. The residues corresponding to the predicted stem are indicated by a line.