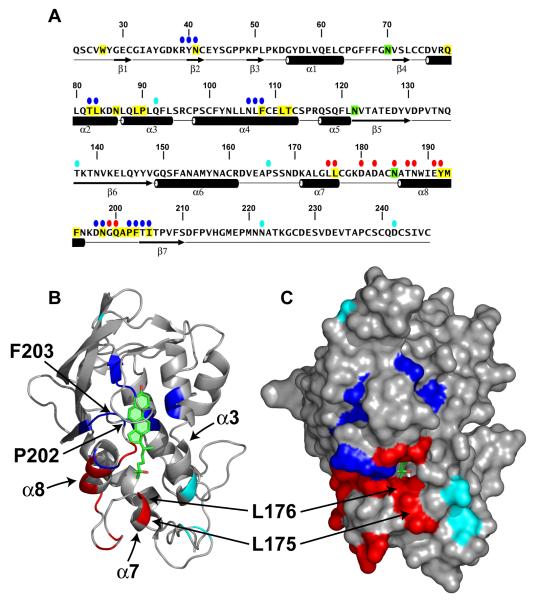
Figure 4. Location of Functionally Important Residues in NPC1(NTD).
(A) Amino acid sequence of NPC1(NTD) with functionally important residues highlighted. Blue ovals denote residues that exhibit decreased binding of cholesterol and 25-HC by >75% when mutated to alanine. Red ovals denote residues that exhibit decreased transfer of cholesterol to liposomes by >70% when mutated to alanine. Cyan ovals denote naturally-occurring mutations in patients with NPC1 disease. Residues that line the binding pocket are shaded yellow. N-linked glycosylation sites that were eliminated are shaded green. The secondary structure of NPC1(NTD) is indicated below the sequence.
(B and C) Ribbon diagram (B) and surface representation (C) of NPC1(NTD), showing the positions of functionally important residues. Bound 25-HC is shown as a stick model in green. Color coding is the same as in (A). The location of the L175, L176, P202, and F203 residues are denoted by arrows.