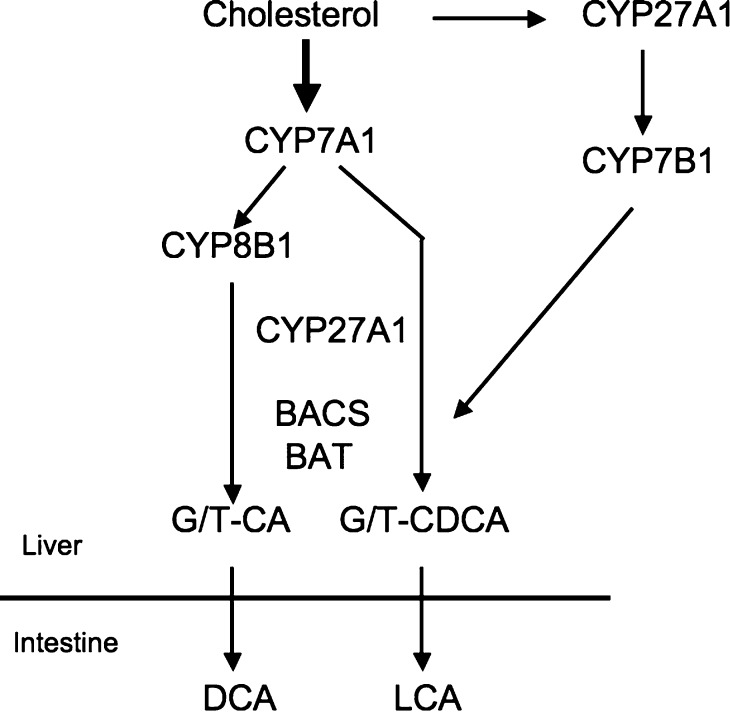
Fig. 1.
Bile acid synthesis. Cholesterol is converted to two primary bile acids in human liver, CA and CDCA. Key regulated enzymes, CYP7A1, CYP8B1, CYP27A1, and CYP7B1, in the pathways are indicated. CYP7A1 initiates the classic (neutral) bile acid biosynthetic pathway in the liver. CYP27A1 initiates the alternative (acidic) pathway in the liver and macrophages. CA and CDCA are conjugated to glycine (G) and taurine (T). BACS and BAT are two key enzymes involved in amino conjugation of bile acids. In the intestine, conjugated CA and CDCA are deconjugated and then dehydroxylated at the 7α-position to the secondary bile acids DCA and LCA, respectively.