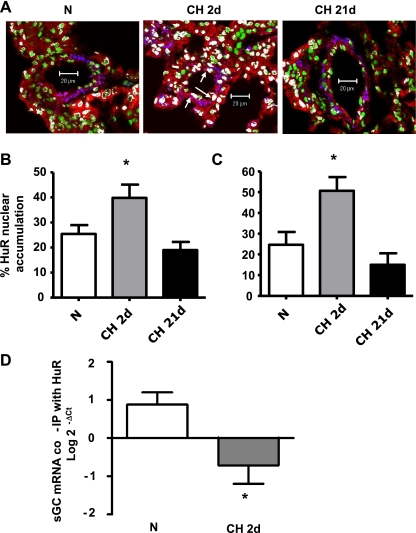
Fig. 4.
Short-term CH (2d) increases HuR nuclear accumulation and decreases HuR/sGC-α1 mRNA coimmunoprecipitation in pulmonary arteries. A: lung sections from mice exposed to N and CH for 2d or 21d were costained with the DNA-binding dye SYTOX (green) and anti-HuR (red) and anti-SM α-actin (blue) antibodies. Representative images show nuclear colocalization of HuR (white) in FVBN mice. Arrows indicate examples of HuR-positive nuclei in pulmonary arteries. Scale bar, 20 μm. Data are summaries of HuR nuclear accumulation in FVBN mice (B) and Balb/C NFATc3 WT mice (C). Values are means ± SE; n = 23–38 arteries from 4 animals/group. *P < 0.05 vs. N. D: HuR was immunoprecipitated (IP) in pulmonary arteries from N- and CH (2d)-exposed NFATc3 WT mice. sGC-α1 mRNA bound to it was amplified by real-time PCR. Input RNA was used as reference control.