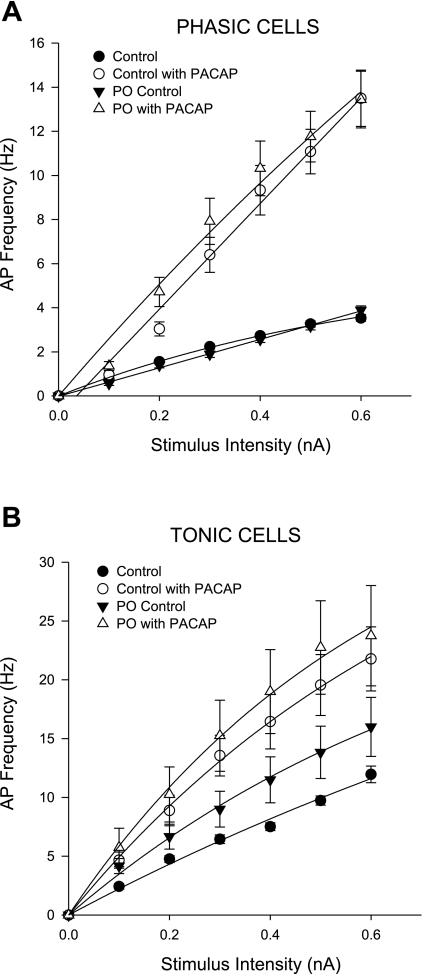
Fig. 4.
The PACAP-induced increase in neuronal excitability is unchanged with pressure overload. Cells from PO preparations showed no change in the responses to exogenous PACAP application compared with control preparations. PACAP application induces an increase in the frequency of evoked APs in both phasic (A, top) and tonic (B, bottom) neurons. There was no significant difference in the frequency of APs produced at increasing stimulus intensities in PO vs. control preparations in the absence of PACAP. Similarly, there were no significant differences in the frequency of APs produced following PACAP application in untreated cells from PO preparations compared with controls. All frequency vs. stimuli curves were best fit with a single exponential curve, with R2 > 0.99.