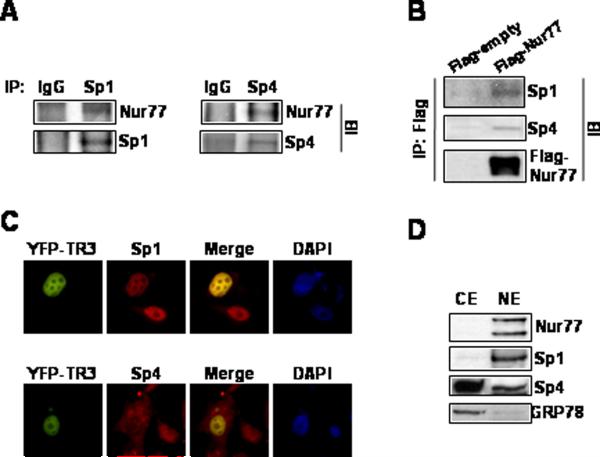
Figure 6.
Association of Nur77 with Sp1 and Sp4. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation. Endogenous Sp1 and Sp4 were immunoprecipitated with each of the antibodies and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blots using anti-Nur77 antibody as outlined in the Materials and Methods. (B) Cells were transfected with Flag-tagged Nur77 or empty vector, whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibodies and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blots using anti-Sp1 and anti-Sp4 antibodies. (C) Immunoprecipitation with Flag antibodies. Subcellular colocalization of Nur77, Sp1, and Sp4. Cells were transiently transfected with pEYFP-Nur77 and 24 hr after transfection, cells were fixed, incubated with anti-Sp1 or anti-Sp4, and visualized as described in the Materials and Methods. The colocalization of Nur77 with Sp1 and Sp4 are depicted in the merged image. (D) Distribution of Nur77, Sp1, and Sp4 in subcellular fractions. Cytosolic and nuclear extracts were obtained and analyzed by Western blots as described in the Materials and Methods. Sp1, a nuclear protein, also serves as a nuclear protein marker and GRP78, a resident protein of endoplasmic reticulum, serves as a cytosolic protein marker.