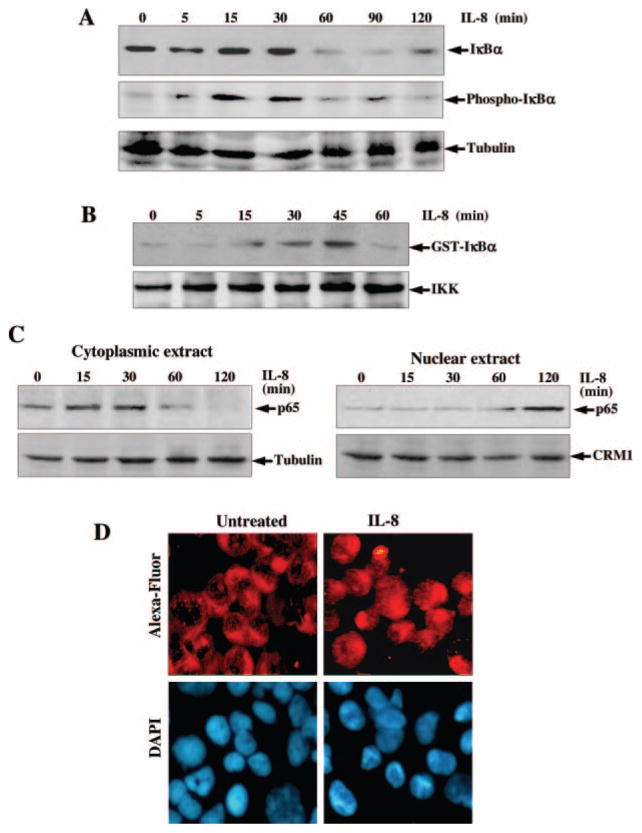
Fig. 2.
A, effect of IL-8 on phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα. U-937 cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml IL-8 for different times. Cytoplasmic extracts (50 μg/sample) were assayed for IκBα and phospho-IκBα by Western blot. The same blot was reprobed with anti-tubulin antibody. B, effect of IL-8 on IKK activation. U-937 cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml IL-8 for different times, and whole cell extracts were prepared, 250 μg of protein were immunoprecipitated with anti-IKKα antibody, and IKK was assayed using GST-IκBα as substrate protein. 50 μg of protein were analyzed in 10% SDS-PAGE to detect IKKα by Western blot. C and D, effect of IL-8 on translocation of p65. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were analyzed in 10% SDS-PAGE and assayed for p65 (C) by Western blot. The gel, which ran with cytoplasmic extracts, was reprobed with anti-tubulin antibody, and the gel with nuclear extracts was reprobed with anti-CRM1 antibody. U-937 cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml IL-8 for 2 h. Cells were subjected to immunocytochemistry (D) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Alexa-Fluor took on a red color to detect p65 (upper panel) and DAPI took on a blue color for the nucleus (lower panel).