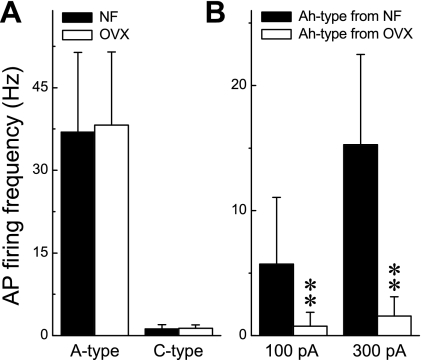
Fig. 2.
Contrasting excitability of VGN identified as myelinated A and Ah type and unmyelinated C type between intact and OVX rats. APs were elicited by a step depolarizing current, and neuronal excitability was quantified as average action potential firing frequency (APFF) over the 1,000-ms step. A: for 200- and 600-pA step currents applied to myelinated A-type and unmyelinated C-type VGN, respectively, there was no significant difference in the APFF between intact (NF) and OVX females. B: APFF of myelinated Ah-type VGN from OVX females were markedly reduced compared with APFF from intact females. Data are means ± SD. **P < 0.01 vs. intact females.