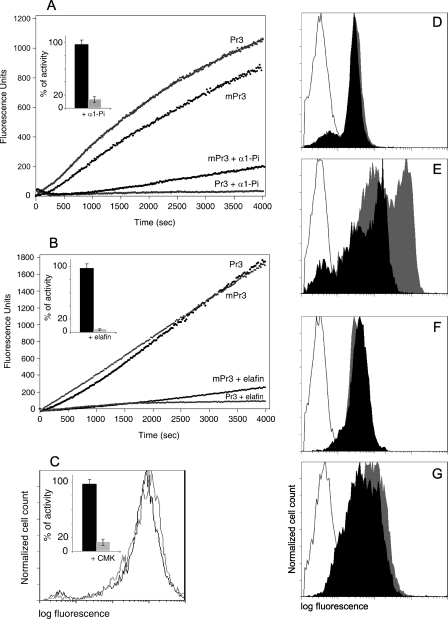
FIGURE 4.
Fate of Pr3 at the neutrophil surface. Activities of soluble Pr3 and mPr3 prior to and after adding a molar excess of α1-Pi (A) or elafin (B). Insets show the percentages of inhibition after incubation for 1 h (mean of three analyses). Neutrophil samples in A and B are from two different healthy donors. Shown is the flow cytometry analysis of membrane-bound Pr3 on mPr3high quiescent blood neutrophils (D) and triggered neutrophils (E) before (gray peak) and after (black peak) incubation with α1-Pi, quiescent and triggered neutrophils before (gray peak) and after (black peak) incubation with elafin (F and G), and triggered neutrophils before (gray line) and after (black line) incubation with MeO-Suc-AAPA-CMK (C). The control isotype is depicted by a gray line (D–G). Neutrophils were labeled with MCPR3–2 mAb and revealed by FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG to visualize cell surface Pr3. The displacement of fluorescence in E shows that induced Pr3 is removed from the cell surface by α1-Pi but not by elafin (G) and by MeO-Suc-AAPA-CMK (C), whereas constitutive Pr3 is not (D).