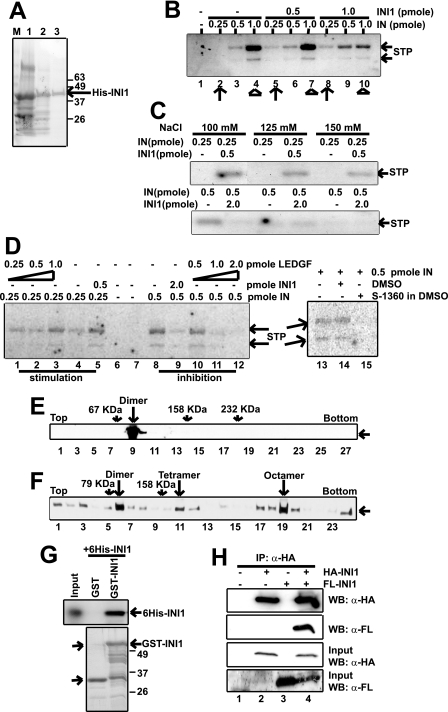
FIGURE 1.
Active INI1 is a multimer. A, Coomassie Blue staining of protein preparations from different stages of His-INI1 purification, viz. Ni-NTA, hydroxylapatite, and Mono-Q Sepharose. B, in vitro integration assay with increasing amounts of IN (0.25, 0.5, and 1 pmol) and INI1 (0.5 and 1 pmol) as indicated. C, in vitro integration assay at physiological salt concentration as indicated. For stimulation, 0.25 pmol of IN and 0.5 pmol of INI1 were used. For inhibition, 0.5 pmol of IN and 2 pmol of INI1 were used. D, in vitro integration assay with increasing concentrations of IN (0.25 and 0.5 pmol) and LEDGF (0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 pmol) as indicated and with 5.3 μm integrase inhibitor S-1360. Lane 14 is a control for the addition of inhibitor, where vehicle (DMSO) has been added. E, 15–35% glycerol gradient centrifugation of <5 nm Mono-Q His-INI1. Fractions were analyzed by Western blot using anti-His antibody as probe. BSA, aldolase, and catalase were run in parallel gradients. F, 15–35% glycerol gradient centrifugation of >100 nm Mono-Q His-INI1. Analysis was carried out as described in E. Aldolase was used as a molecular weight marker. G, GST pulldown assay using GST, GST-tagged INI1 immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads, and purified His-INI1. Bound proteins were analyzed by Western blot using anti-His antibody as probe. H, coimmunoprecipitation (IP) of FLAG-INI1 using HA-INI1 as bait. 293T cells were transfected with either HA-INI1 or FLAG-INI1 or both, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA agarose. Immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by Western blot (WB) using anti-FLAG and anti-HA antibodies as probes. STP, strand transfer product.