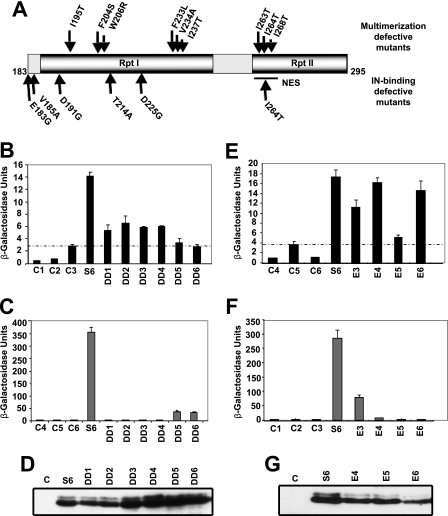
FIGURE 3.
Isolation and characterization of INI1-(183–294) mutants defective for multimerization. Amino acid residues involved in multimerization of INI1 are overlapping but distinct from those involved in IN binding. A, identity and position of multimerization-defective mutants of INI1-(183–294). B, quantitative yeast two-hybrid assay (β-galactosidase/ONPG assay) of GAL4AD-fused wild type and mutant INI1-(183–294) with full-length INI1 fused to LexADBD. C, quantitative yeast two-hybrid assay (β-galactosidase/ONPG assay) of GAL4AD-fused wild type and mutant INI1-(183–294) with LexADBD-fused wild type IN. D, Western blot analysis of wild type and mutant INI1-(183–294) containing yeast extracts using anti-GAL4AD antibody as probe. E, quantitative yeast two-hybrid assay (β-galactosidase/ONPG assay) of GAL4AD-fused wild type and mutant INI1-(183–294) and LexADBD-fused wild type INI1. F, quantitative yeast two-hybrid assay (β-galactosidase/ONPG assay) of GAL4AD-fused wild type and mutant INI1-(183–294) and LexADBD-fused wild type IN. G, Western blot analysis of wild type and mutant INI1-(183–294) containing yeast extracts using anti-GAL4AD antibody as probe.