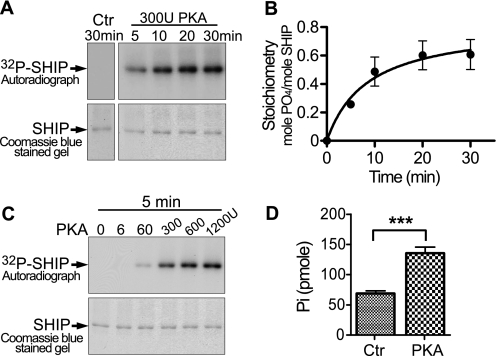
FIGURE 2.
PKA can phosphorylate SHIP1 in vitro and increase its activity. A, upper panel, autoradiograph showing time-dependent phosphorylation of SHIP1 by PKA. Each reaction contained 70 ng of SHIP1 and was incubated with 300 units of PKA for the indicated time. Lower panel, Coomassie Blue-stained 8% SDS gel used to make autoradiograph. B, the bands cut from the gel in A were counted in a scintillation counter. The stoichiometry was calculated from the known specific activity of [32P]ATP used in the reaction mixture and the amount of 32P in each gel slice. C, PKA-dependent phosphorylation of SHIP1. Pure SHIP1 was phosphorylated with the indicated concentration of PKA for 5 min. D, activity of native SHIP1 and PKA-treated SHIP1 was compared following treatment with 300 units of PKA for 10 min. PKA significantly increased activity. ***, p < 0.001 (n = 6). Ctr, control.