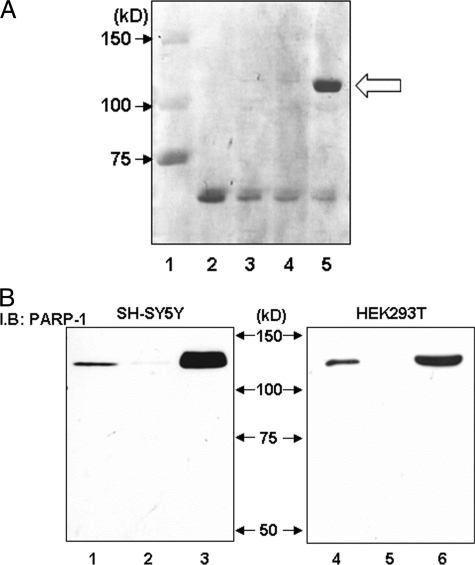
FIGURE 3.
Purification of specific binding protein to the G−172 → T region and confirmation of identified PARP-1 protein using specific antibody in Western blotting. A, specific protein was purified using biotin-labeled T−172 probe, avidin-agarose beads, and HEK293T-derived nuclear extract and was applied to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Avidin-agarose beads were pretreated by bovine serum to prevent nonspecific protein binding. Loaded sample was as follows: lane 1, protein molecular weight standards; lane 2, 1.0 μg of bovine serum; lane 3, purified protein with biotin-labeled T−172 probe/without nuclear extracts; lane 4, purified protein with non-biotin-labeled T−172 probe and HEK293T-derived nuclear extracts; lane 5, purified protein with biotin-labeled T−172 probe and HEK293T-derived nuclear extracts. In lane 5 only, specific DNA-binding protein was observed at 120 kDa, as indicated by the arrow. B, cell lysate or purified protein from SH-SY5Y or HEK293T was loaded to SDS-PAGE and was investigated by immunoblotting (I.B.) using anti-PARP-1 antibody. Lanes 1–3, nuclear protein was extracted from SH-SY5Y; lanes 4–6, nuclear protein was extracted from HEK293T. Lanes 1 and 4, 1.0 μg of unpurified nuclear protein; lanes 2 and 5, purified protein with non-biotin-labeled T−172 probe; lanes 3 and 6, purified protein with biotin-labeled T−172 probe. These experiments were independently performed three times or more.