Table 1.
Conditions for oxidative cycloaddition of 12.
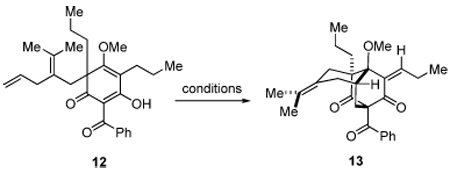 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | oxidant (equiv)a | solvent | time (h) | % yield |
| 1 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | AcOH | 4 | 66b |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 2 | Mn(OAc)3 (1.0) | AcOH | 6 | 31d |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 3 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | AcOH | 16 | tracec |
| 4 | Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | AcOH | 16 | --d |
| 5 | Mn(OAc)3 (0.1) | AcOH | 16 | traced |
| 6 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | THF | 16 | --c |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 7 | Mn(OAc)3 (2.1) | MeCN | 16 | --c |
| Cu(OAc)2 (1.0) | ||||
| 8 | Ce(NH4)2(NO3)6 (2.0) | MeCN | 3 | --e |
| 9 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.2) | MeCN | 16 | NRd |
All reactions were carried out at ambient temperature except when noted; Mn(OAc)3·2H2O, and Cu(OAc)2·H2O were used;
Isolated as a 5:1 mixture of olefin isomers (1H NMR);
Slow decomposition of the starting material occurred.
Starting material was recovered unreacted.
Reaction performed at −20 °C and resulted in a complex mixture of products.
