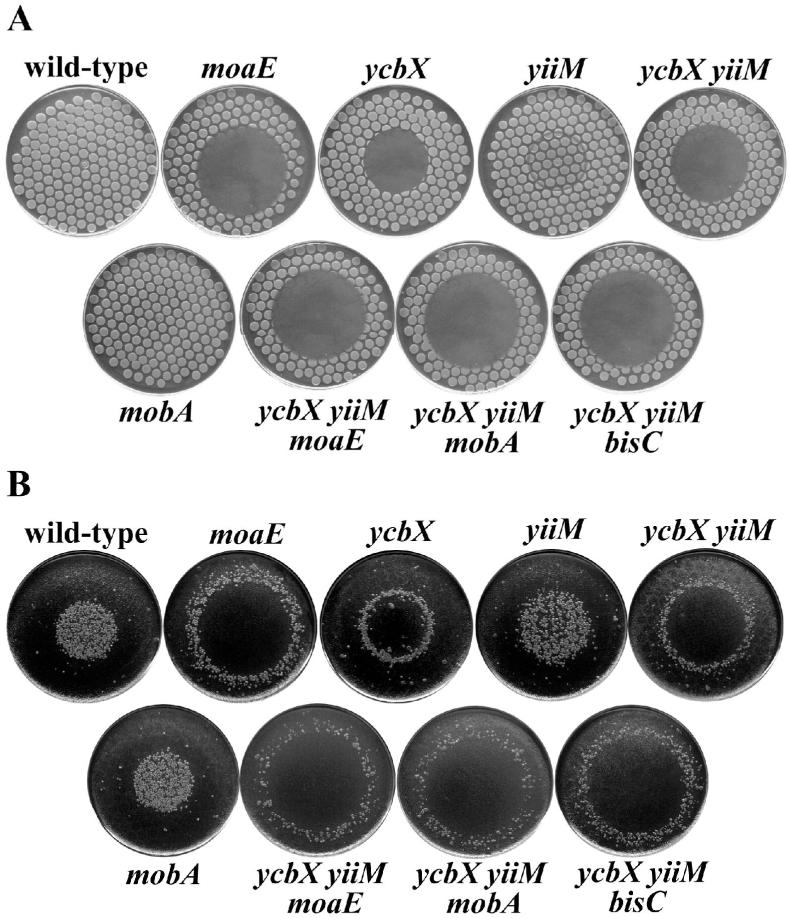
Fig. 1.
HAP-induced killing (A) and mutagenesis (B) for various E. coli mutants. The strains used were wild-type (NR10836), moaE (NR15996), ycbX (NR15873), yiiM (NR15871), ycbX yiiM (NR15876), mobA (NR15994), ycbX yiiM moaE (NR16023), ycbX yiiM mobA (NR16028), and ycbX yiiM bisC (NR16047). Cells were spotted on a minimal medium plate using a multi-prong replicator device, and 50 μg of HAP was spotted onto the center of each plate (see Experimental procedures). The plates, after overnight incubation, are shown in panel A. These plates were replica-plated onto LB plates containing rifampicin and incubated overnight (panel B).