Fig. 5. Regulation of mouse Ntcp by dexamethasone and Bsep by spironolactone.
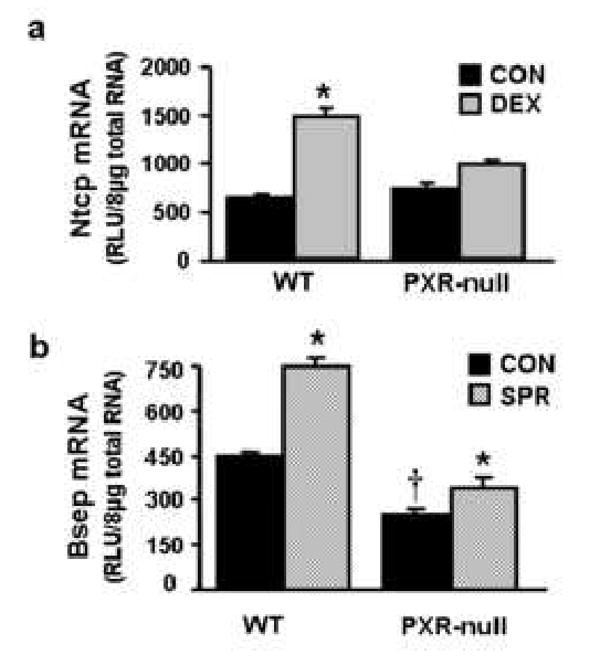
a) Regulation of mouse Ntcp by dexamethasone in wild-type mice and PXR-null mice.Wild-type mice and PXR-null mice (n=4-6/group) were treated once daily for 4 days with 50mg/kg dexamethasone. Control group received corn oil. On day 5, liver tissues were removed and used for total RNA isolation. Individual total RNA sample (n=4-6 mice) were analyzed by bDNA assay. The solid, black bar represents the data from the control group; the gray bar represents the data from mice after treatment with 50 mg/kg dexamethasone. b) Regulation of mouse Bsep by spironolactone in wild-type mice and PXR-null mice. Wild-type and PXR-null mice (n=5/group) were treated once daily for 4 days with corn oil (control) or spironolactone (200 mg/kg, ip in corn oil). On day 5, liver tissues were removed and used for total RNA isolation. Total RNA from five treated male livers was analyzed by the bDNA assay. All data were expressed as mean ± S.E.M. for five mice in each group. Asterisk indicates statistically significant difference between treated and control mice (p < 0.05). Single dragger (†) indicates statistically significant difference between wild-type and PXR-null mice (p < 0.05).
