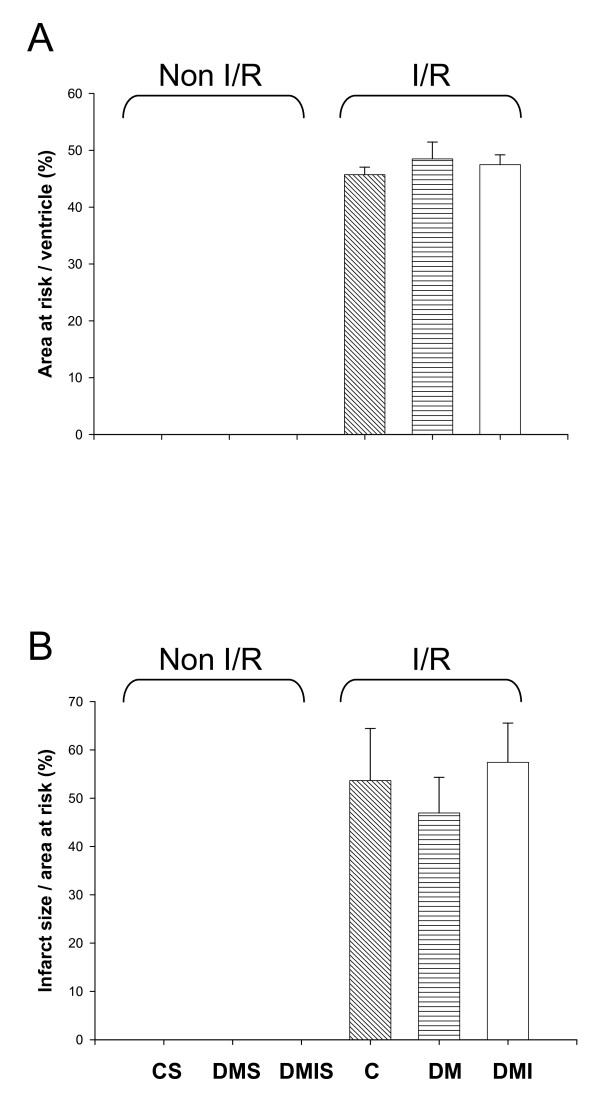
Figure 2.
The effects of diabetes on I/R-induced myocardial infarction were evaluated in the age-matched controlled (n = 7), STZ-diabetic (n = 10), and insulin-treated diabetic (n = 9) rats. SD rats were subjected to 1 h of left coronary artery occlusion and 3 h of reperfusion. The level of myocardial infarction was determined by the triphenyl tetrazolium chloride-Evan's blue technique. (A) Ratio of area at risk to total ventricle. (B) Ratio of infarct size to area at risk. Data were expressed as mean ± SE. C, age-matched control; CS, control sham; DM, STZ-induced diabetes; DMS, DM sham; DMI, diabetes treated with insulin (4 IU/day for 5 days); DMIS, DMI sham; I/R, myocardial ischemia 1 h following by a 3 h of reperfusion.