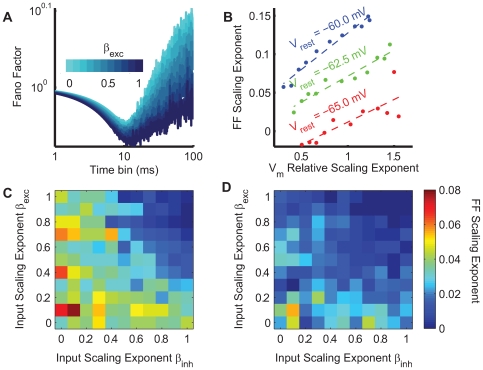
Figure 7. Relation between the 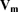 frequency-scaling exponent and that measured from the Fano Factor (FF) of the output spike train.
frequency-scaling exponent and that measured from the Fano Factor (FF) of the output spike train.
A Example of the FF changes as a function of time bin, for different input parameters 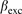 . The resting potential
. The resting potential 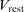 has been set to −60 mV to ensure a large enough number of spikes. The synchrony parameter is fixed at 6%. B Relation between spiking and relative
has been set to −60 mV to ensure a large enough number of spikes. The synchrony parameter is fixed at 6%. B Relation between spiking and relative 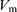 frequency-scaling exponents for different resting potentials (
frequency-scaling exponents for different resting potentials (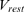 = −65 mV, −62.5 mV and −60 mV). C,D Fano Factor frequency-scaling exponents as a bivariate function of excitatory and inhibitory
= −65 mV, −62.5 mV and −60 mV). C,D Fano Factor frequency-scaling exponents as a bivariate function of excitatory and inhibitory 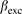 and
and 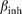 parameters, in the absence of excitatory-inhibitory correlation and for and
parameters, in the absence of excitatory-inhibitory correlation and for and 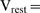 −65 mV (C), and in the case of 40% of correlation and
−65 mV (C), and in the case of 40% of correlation and 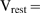 −62.5 mV (D). In this latter case,
−62.5 mV (D). In this latter case, 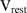 has been increased by a few mV to ensure a reasonable level of spiking activity.
has been increased by a few mV to ensure a reasonable level of spiking activity.