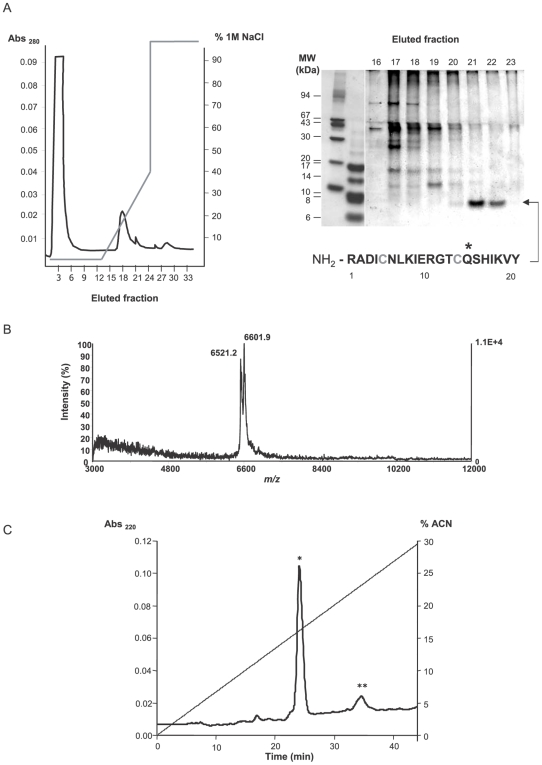
Figure 2. Purification of EgKU-1 and EgKU-8 from a protoscolex extract.
(A) Fractionation of cationic protoscolex proteins. Left panel, Chromatography profile (MonoS column; pH 7); elution was with increasing NaCl concentrations. Right panel, Tricine SDS-PAGE of eluted fractions under non-reducing conditions; the gel was Coomassie-stained. N-terminal sequencing of the 7 kDa band identified EgKU-1 in fractions 21 and 22 (see Figure 1A). Conserved Cys are in grey and the putative P1 site marked with an asterisk. (B) MALDI-TOF MS of EgKU-1containing fractions. The peak at m/z 6601.9 matched the MH+ value predicted for EgKU-1 (6600.5 Da); similarly, the 6521.2 signal indicated that the fractions also contained EgKU-8 (MH+ = 6520.4 Da). MW estimation was from cDNA predicted sequences, considering that conserved Cys form disulfide bonds (see Table S1). (C) Separation of EgKU-1 and EgKU-8 by rpHPLC. A pool of the ion exchange fractions containing the 7 kDa band was loaded onto a C8 column. A major and a minor peak were eluted with acetonitrile (ACN) in 0.07% trifluoroacetic acid, at about 16% (*) and 24% (**) ACN. By MALDI-TOF MS, each peak was found to contain one predominant component corresponding, respectively, to EgKU-1 and EgKU-8, as specified in (B).