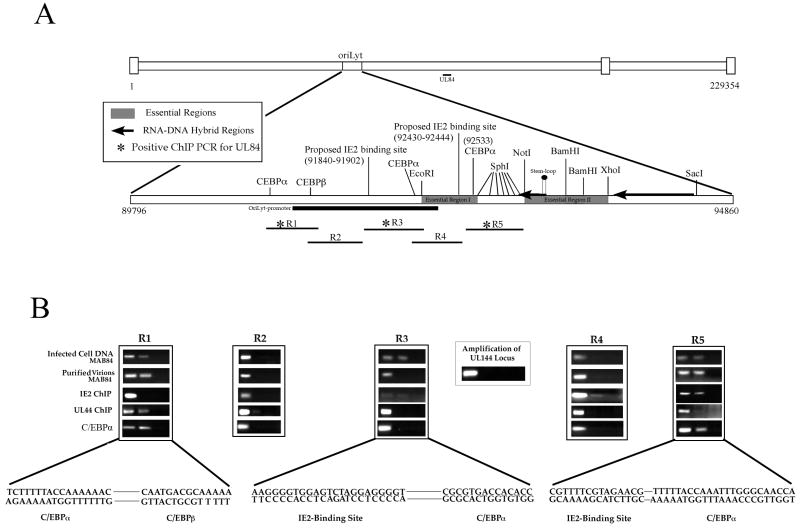
Figure 1. Interaction of UL84, UL44, IE2 and C/EBPα with oriLyt.
(A) Schematic of HCMV genome showing the location of oriLyt and the positions of three essential regions, various restriction enzyme recognition sites, RNA/DNA hybrids, C/EBPα/β, IE2-binding sites, oriLyt promoter region and the RNA stem-loop structure. Also shown are the relative locations of PCR primers used for ChIP assays for DNA isolated from infected cells and purified virions. (B) ChIP assays showing the interaction of UL84, IE2, UL44 and C/EBPα with various regions of oriLyt. Infected cells were prepared as described and specific antibodies to UL84 (Virusys), IE2 (Vancouver Biotech), UL44 (Bill Britt) or C/EBPα (Santa Cruz) were used for immunoprecipitations. PCR primers from regions 1-5 are shown above each ChIP assay gel. The lanes of each ChIP assay are as follows: 1, PCR product from input DNA; 2, PCR product from immunoprecipitations using specific antibodies shown to the left of the figure; 3, PCR product from immunoprecipitations using an unrelated antibody that was the same isotype as the test antibody. Also shown is a PCR amplification of the HCMV UL144 loci from samples immunoprecipitated using the anti-UL84 antibody. Lanes: 1, PCR product from input DNA; 2, PCR product from immunoprecipitations using the anti-UL84 antibody; 3, PCR product from immunoprecipitations using an unrelated antibody that was the same isotype as the test antibody. Solid line shows sequences gaps.