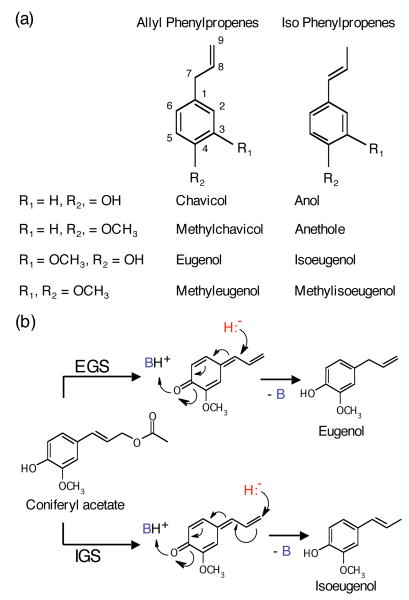
Figure 1. Structures of representative phenylpropenes and reaction mechanism of EGS and IGS enzymes.
(a) Structures of chavicol, anol, eugenol, isoeugenol, and their methylated derivatives. The carbon numbering system used in the text is shown.
(b) The reaction mechanism of EGS and IGS uses a quinone methide intermediate (Louie et al., 2007). B (in blue) represents a general base consisting of K132 and a bridging water molecule. H- (in red) represents the hydride transferred from NADPH.