Figure 3. Sequence comparisons of CbIGS1, CbEGS1, CbEGS2, and representative PIP proteins.
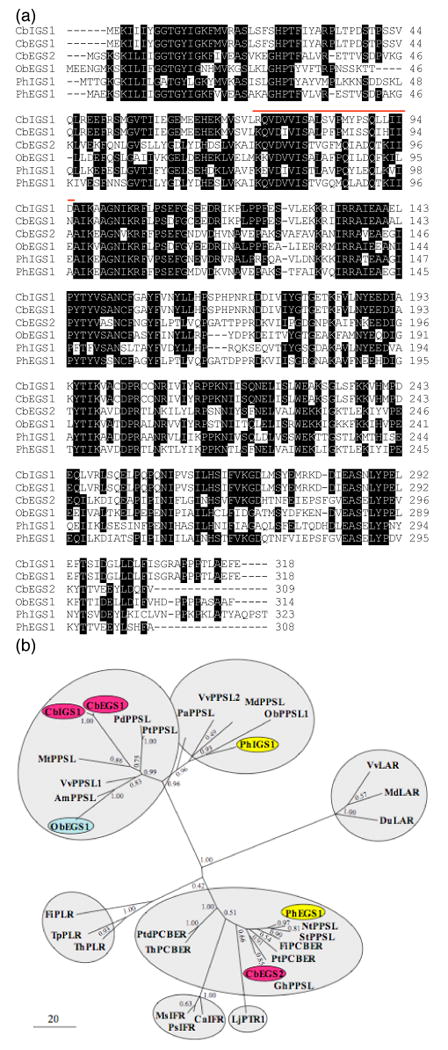
(a) A comparison of amino acid sequences of C. breweri CbIGS1, CbEGS1, and CbEGS2, petunia PhIGS1 and PhEGS1, and basil ObEGS1. White letters on black background represent identical residues in at least four sequences. The region highly divergent between CbEGS1 and CbIGS1 (positions 73-95) is indicated by a red line.
(b) Phylogenetic analysis of selected protein sequences in the PIP family showing an unrooted maximum likelihood tree. The scale indicates the number of substitutions per site. In addition to IGS/EGS-like proteins, the PIP family includes pinoresinol-lariciresinol reductases (PLR), isoflavone reductases (IFR), phenylcoumaran benzylic ether reductases (PCBER), leucocyanidin reductase (LAR), and pterocarpan reductase (PTR). Proteins biochemically characterized in C. breweri, basil, and petunia are shown on red, blue, and yellow background, respectively. Proteins for which no specific activity has been assigned are designated here as PPSL (phenylpropene synthase-like). The position of the PLR branch is uncertain (bootstrap value of 0.42), and in the neighbor-joining and maximum parsimony trees (not shown) it is closer to the ObEGS1/PhIGS1 clades. The only other disagreement among the three trees - the positions of the IFR branch and the PTR branch, which is also uncertain in the maximum likelihood tree - is discussed in the text. Am, Antirrhinum majus; Ca, Cicer arietinum; Cb, Clarkia breweri; Du, Desmodium uncinatum; Fi, Forsythia intermedia; Gh, Gossypium hirsutum; Lj, Lotus japonica; Md, Malus domestica; Ms, Medicago sativa; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Nt, Nicotiana tabacum; Ob, Ocimum basilicum; Pa, Persea americana; Pd, Populus deltoides; Ph, Petunia hybrida; Ps, Pisum sativum; Pt, Populus trichocarpa; Ptd, Pinus taeda; St, Solanum tuberosum; Th, Tsuga heterophylla; Tp, Thuja plicata; Vv, Vitis vinifera. The accession numbers of the proteins are given in Supplementary Table 2.
