Figure 9. Views of the active sites of ObEGS1, ObEGS1 (F85V, I88Y), and the CbEGS1.
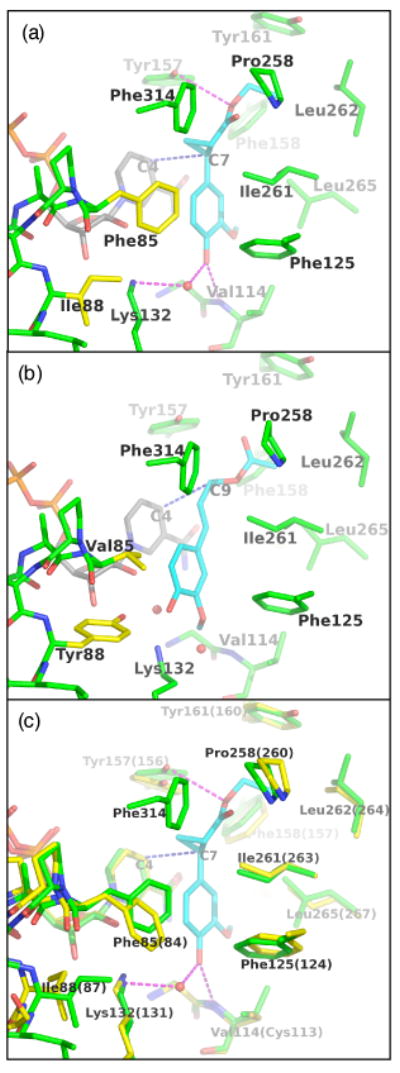
(a) ObEGS1 complexed with EMDF (Louie et al., 2007). Green - EGS active site residues; yellow - sites of amino-acid substitutions; gray - NADP+ cofactor; cyan - substrate.
(b) Crystal structure of ObEGS1 (F85V, I88Y) with modeled coniferyl acetate. The binding of the substrate was modeled manually based initially on the observed binding mode of EMDF with wild-type ObEGS1, and adjusted to fill the space vacated by F85 side chain and to form a hydrogen bond between Y88 and the substrate C4-OH. Color coding is as in (a).
(c) Comparison of the active sites of ObEGS1 (green) and CbEGS1 (yellow, residue numbering in parentheses) superimposed. EMDF is shown from the complex with ObEGS1.
