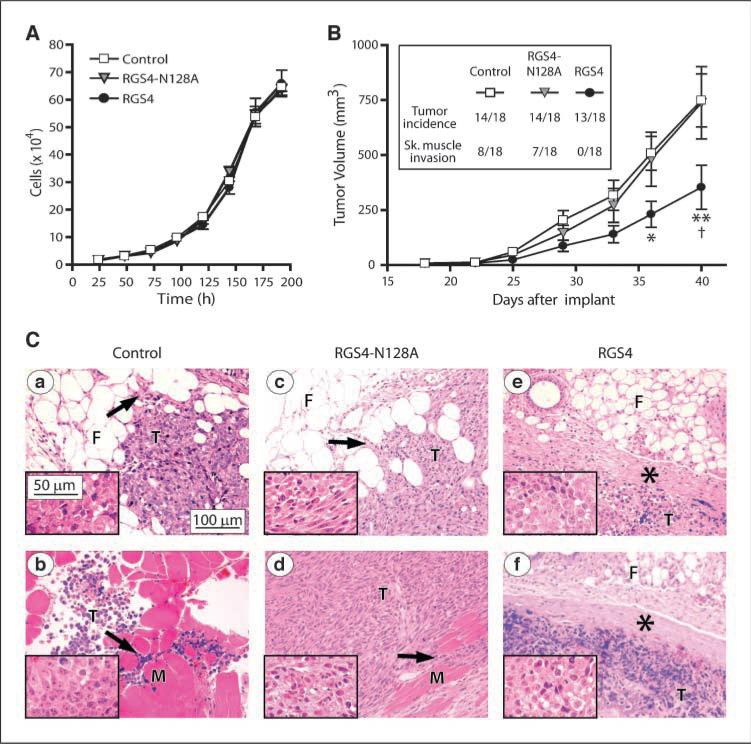
Figure 2.
RGS4 inhibits breast tumor growth and suppresses tumor invasion in nude mice. A, in vitro growth of MDA-MB-231 control cells or cells stably expressing RGS4 or RGS4-N128A. Points, mean (n = 4 triplicate experiments); bars, SE. B, in vivo tumor growth derived from MDA-MB-231 cell variants injected into mouse mammary fat pads (n = 18 mice per group; inset, tumor incidence and skeletal muscle invasion). Points, mean for formed tumors; bars, SE. *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.001 compared with control, †, P < 0.001 compared with RGS4-N128A using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni comparison of means. C, representative H&E-stained micrographs of tumor tissue from mice injected with MDA-MB-231 control cells showing (a) mammary fat pad and (b) skeletal muscle invasion, RGS4-N128A–expressing cells showing (c) mammary fat pad and (d) skeletal muscle invasion, and RGS4-expressing cells showing well demarcated tumor boundaries (e and f, asterisks). Arrows, infiltration of the tumor cells (T) into the fibroadipose tissue (F) or skeletal muscle (M). Insets, higher magnification images of the tumor cells.