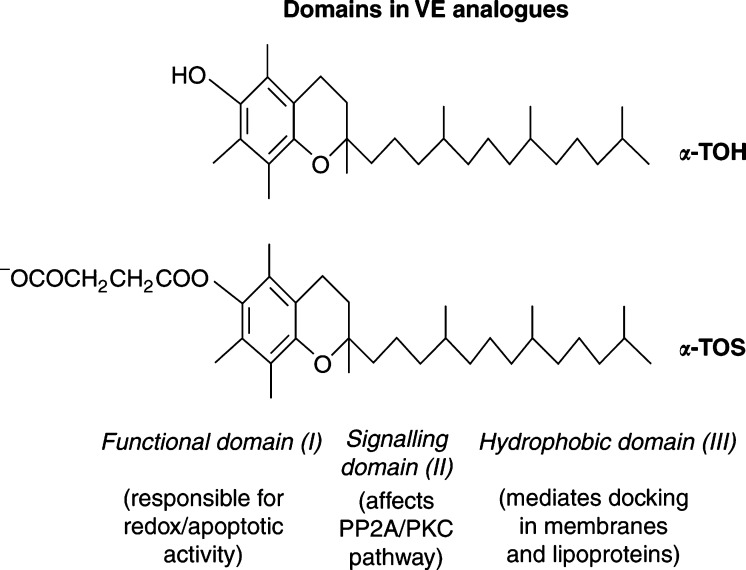
Figure 1.
Functional domains in the molecule of VE. Vitamin E analogues (represented here by α-TOH and α-TOS) comprise three distinct domains, each responsible for a separate ‘function’ of the agent. Domain I, the functional domain, decides whether the compound is redox-active or redox-inactive. Domains II, the signalling domain, is responsible for effects of the analogues such as deregulation of the protein kinase C/protein phosphatase 2A pathway. Domain III, the hydrophobic domain, is responsible for docking of VE analogues in biological membranes and lipoproteins.