Figure 3.
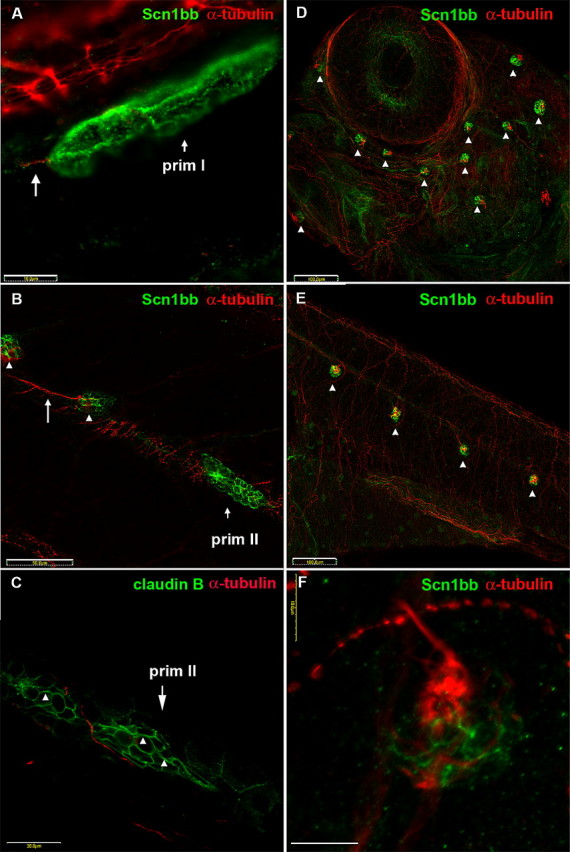
Scn1bb is expressed in migrating primordia and neuromasts of the lateral line system. A–C, Migrating primordia and newly formed neuromasts express Schn1bb protein. A, Immunocytochemistry reveals nonoverlapping expression of both Scn1bb (green) and acetylated α-tubulin (red) proteins in the migrating prim I lateral line primordium of 28 hpf embryos. The octavolateralis system axons (long arrow), that trail prim I, display acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, In 5 dpf larvae, the prim II lateral line primordium and newly deposited neuromasts express Scn1bb (green). However, prim II (short arrow) and newly deposited neuromasts (arrowheads) do not express acetylated α-tubulin. In contrast, an innervating neurite (long arrow) is positive for acetylated α-tubulin immunoreactivity. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, Similar to Scn1bb, claudin b (arrowheads) is present in prim II in a complementary pattern to anti-acetylated α-tubulin. Scale bar, 50 μm. D–F, ALL and PLL neuromasts express Scn1bb protein. D, In 5 dpf embryos, anti-Scn1bb (green) specifically reveals neuromasts of the ALL (arrowheads). Scn1bb and acetylated α-tubulin (red) are expressed in different domains of the ALL neuromasts. Anti-acetylated α-tubulin marks the kinocilia of ALL neuromasts. Scale bar, 100 μm. E, In 5 dpf embryos, anti-Scn1bb (green) also is present within the neuromasts of the PLL (arrowheads). Similar to the ALL, Scn1bb and acetylated α-tubulin (red) are expressed in different domains of the PLL neuromasts. Scale bar, 100 μm. F, Different cell types within a neuromast express Scn1bb (green) and acetylated α-tubulin (red). Supporting cells display Scn1bb immunoreactivity, whereas hair cells express acetylated α-tubulin (red) in the soma and projecting kinocilia. Scale bar, 10 μm.
