Fig. 1.
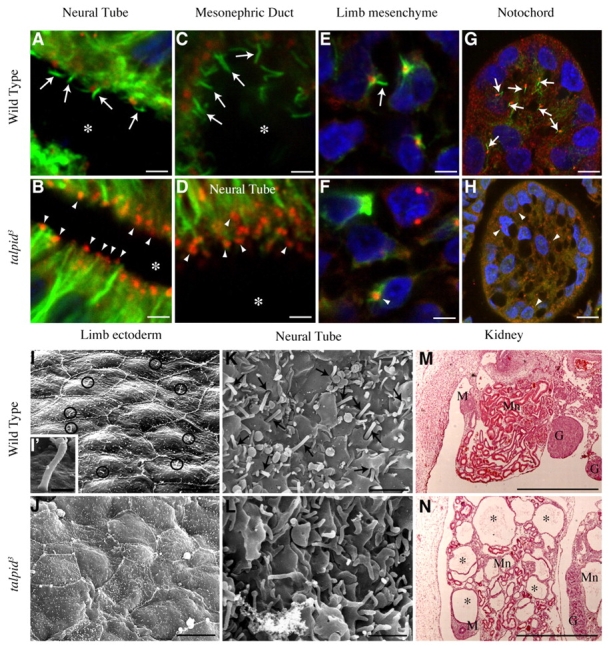
Primary cilia defect in talpid3 mutant embryos. Immunostaining of sections of wild type (A,C,E,G) and talpid3 mutant (B,D,F,H) chicken embryos; anti-γ tubulin (red) for centrosome; anti-acetylated tubulin (green) for ciliary axoneme. (A) Wild-type neural tube, primary cilia (arrows) protruding into lumen (*) from centrosomes. (B,D) talpid3 mutant neural tube (centrosomes are indicated with arrowheads), ciliary axonemes absent, compare with A. (C) Wild-type mesonephric duct; primary cilia (arrows) protruding from centrosomes into lumen (*). (E) Wild-type limb bud; primary cilia on mesenchyme cells (arrow). (F) talpid3 mutant limb bud; centrosomes are indicated with an arrowhead on mesenchyme cells, cilia axonemes are absent (compare with E). (G) Wild-type notochord; primary cilia project from centrosomes (arrows). (H) talpid3 mutant notochord; centrosomes are indicated with arrowheads, ciliary axonemes are absent, compare with G. (I-L) SEM of dorsal surface of wing bud and luminal surface of neural tube from HH24 embryos. (I) Wild-type wing bud; black circles indicate primary cilia. (I′) A higher magnification of primary cilium. (J) talpid3 mutant wing bud; no primary cilia visible. (K) Wild-type neural tube; black arrows indicate primary cilia emerging from pits on apical surface of cells lining lumen. (L) talpid3 mutant neural tube; no primary cilia visible, although there are protrusions from apical surface of cells. (M,N) Sections of the mesonephric kidney (Mn) at 7 days of development stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin. (M) Wild-type embryo. (N) talpid3 mutant embryo, note cysts (*). M, mullerian duct; G, gonad. Scales bars: 5 μm in A-F; 10 μm in G-L; 500 nm in I′; 500 μm in M,N.
