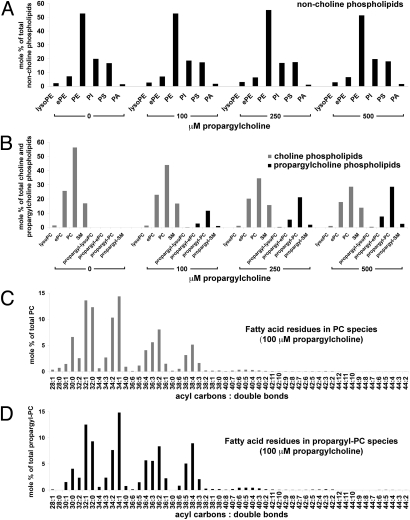
Fig. 2.
Total lipid analysis of propargylcholine-labeled cells. Total lipids isolated from NIH 3T3 cells labeled for 24 h with 0, 100, 250, and 500 μM propargyl-Cho were quantified by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Amounts of various phospholipids are shown as mole percentages of total non-Cho phospholipids (A), total Cho and propargyl-Cho phospholipids (B), total PC species (C), and total propargyl-PC species (D). (A) Distribution of non-Cho phospholipids (lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine, lyso-PE; ether-linked phosphatidylethanolamine, ePE; phosphatidylethanolamine, PE; phosphatidylinositol, PI; phosphatidylserine, PS; phosphatidic acid, PA) in cells labeled with propargyl-Cho. Propargyl-Cho labeling does not significantly affect the relative amount of non-Cho phospholipid classes. (B) Propargyl-Cho incorporates into all phosphatidylcholine (PC) classes (lysoPC; ether-linked PC, ePC; and PC) and into sphingomyelin (SM), proportional to the concentration of propargyl-Cho added to cells. (C and D) In NIH 3T3 cells labeled with 100 μM propargyl-Cho overnight, the sum fatty acid composition of PC species (C) is very similar to that of propargyl-PC species (D). Each PC and propargyl-PC species is identified by two numbers: the first is the sum of acyl carbons, and the second is the sum of double bonds present in the two fatty acid residues of the respective phospholipid species.