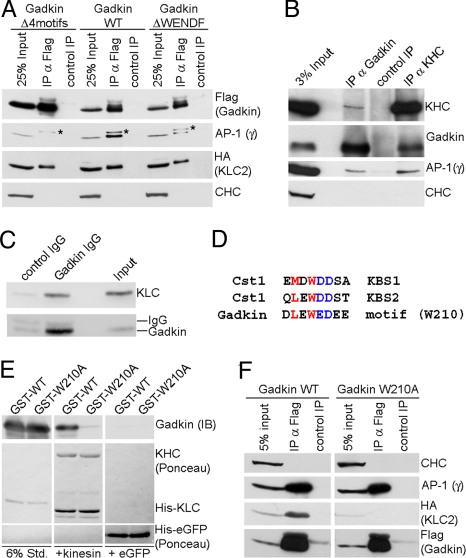
Fig. 5.
Gadkin directly associates with AP-1 and KIF5 via distinct sites. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of AP-1/Gadkin complexes. Lysates of Cos7 cells (200 μg protein) expressing HA-Klc-2 and FLAG-Gadkin WT, ΔWENDF, or Δ4motifs were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG (IP α-FLAG) or anti-c-myc (control IP) antibodies. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting for AP-1γ, CHC, HA, or FLAG. Asterisk, nonspecific band recognized by AP-1γ antibody. (B) Endogenous kinesin-1 and AP-1 coimmunoprecipitate with Gadkin from brain. Control, nonspecific rabbit IgG. Input, 3% of the total material used for immunoprecipitation. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for Gadkin, KHC, AP-1γ, and CHC. (C) Immunoblot analysis of immunoisolated Gadkin-containing organelles as shown in Fig. 2E. Input, 50 μg starting material. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting for Klc2 and Gadkin. (D) Sequence comparison between the kinesin-binding segments (KBS) 1 and 2 of Calsyntenin-1 (Cst1) and a similar motif found in Gadkin. Residues shown to be important for Klc binding (22) are colored. (E) Recombinant kinesin heterotetramers directly bind to purified Gadkin (Δ51), but not to its W210A mutant. Four micrograms purified His10-kinesin heterotetramers or His6-eGFP (control) immobilized on beads were incubated with 2.5 μg GST-Gadkin (Δ51) WT or W210A mutant. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting for Gadkin. Six percent Std, 6% of total amount of purified GST-tagged proteins used. (F) HA-Klc2 coimmunoprecipitates with FLAG-Gadkin WT, but not Gadkin W210A in transfected Cos7 cells (1 mg lysate). Anti-FLAG (α-FLAG IP) or anti-c-myc (control IP) antibodies were used. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for HA, FLAG, AP-1γ, and CHC.