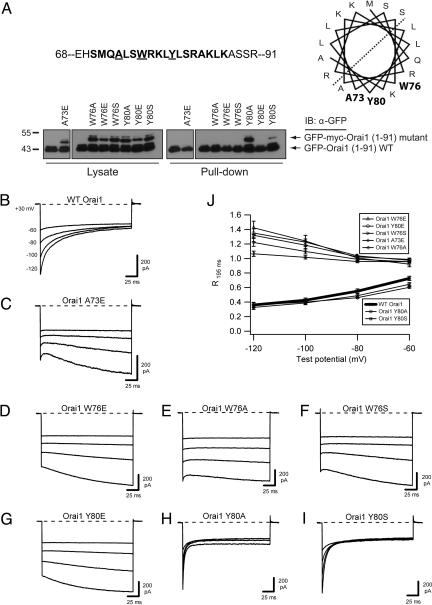
Fig. 4.
Orai1 mutations that prevent CaM binding also block inactivation. (A) Effects of Orai1 mutations on CaM binding. The predicted CaM binding site is shown in bold within the amino acids 68–91 region of Orai1. A73, Y80, and W76 are shown in bold on the predicted hydrophobic face of a helical wheel projection. For the CaM-Sepharose pull-down of WT and mutant Orai11–91 peptides, each lane contains WT peptide and the mutant indicated above. Of the mutant peptides, only Y80A and Y80S retained CaM binding ability. (B–I) Representative currents recorded in 20 mM Ca2+o during pulses to the indicated voltages for WT myc-Orai1 (traces reproduced from Fig. 1A) (B), myc-Orai1 A73E (C), myc-Orai1 W76E (D), myc-Orai1 W76A (E), myc-Orai1 W76S (F), myc-Orai1 Y80E (G), myc-Orai1 Y80A (H), and myc-Orai1 Y80S (I). All cells were cotransfected with WT GFP-STIM11–685. (J) Extent of inactivation, quantified as the residual current remaining at the end of the test pulse (R195 ms = I195 ms/I1.5 ms), plotted against test potential. Peak currents were measured at 1.5 rather than 3 ms because of the rapid inactivation kinetics of Orai1 Y80A and Y80S (Fig. S8). Each point shows the mean ± SEM of five to six cells.