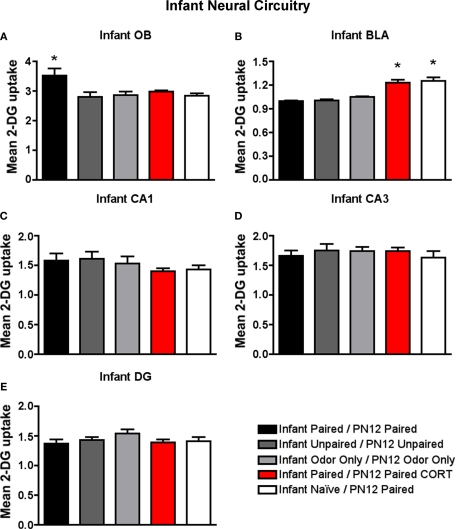
Figure 5.
14C 2-DG autoradiography was used to assess brain areas previously shown to be important for either early life attachment/preference learning (olfactory bulb) or avoidance/fear learning (amygdala). These data compliment behavioral data in Figure 3. Pups were trained daily from PN8–12 or conditioned only on PN12 (Infant Naïve/PN12 Paired) (n = 5–7/group). 2-DG autoradiography during the last odor-shock conditioning session on PN12 showed that (A) Infant Paired/PN12 Paired odor-shock pups exhibit activation in the odor-specific loci of the olfactory bulb (OB) compared to Infant Naïve/PN12 Paired pups that we conditioned only on PN12, (B) Pups receiving odor-shock conditioning for the first time (Infant Naïve/PN12 Paired) or after five sessions but given a PN12 CORT injections (Infant Paired/PN12 Paired CORT) showed increase 2-DG uptake of the amygdala's basolateral complex (BLA), and no statistical differences in 2-DG uptake were found for hippocampal subareas: CA1 (C), CA3 (D) and DG (E). Asterisk represents a significant difference from each of the other groups (p < 0.05).