Figure 3.
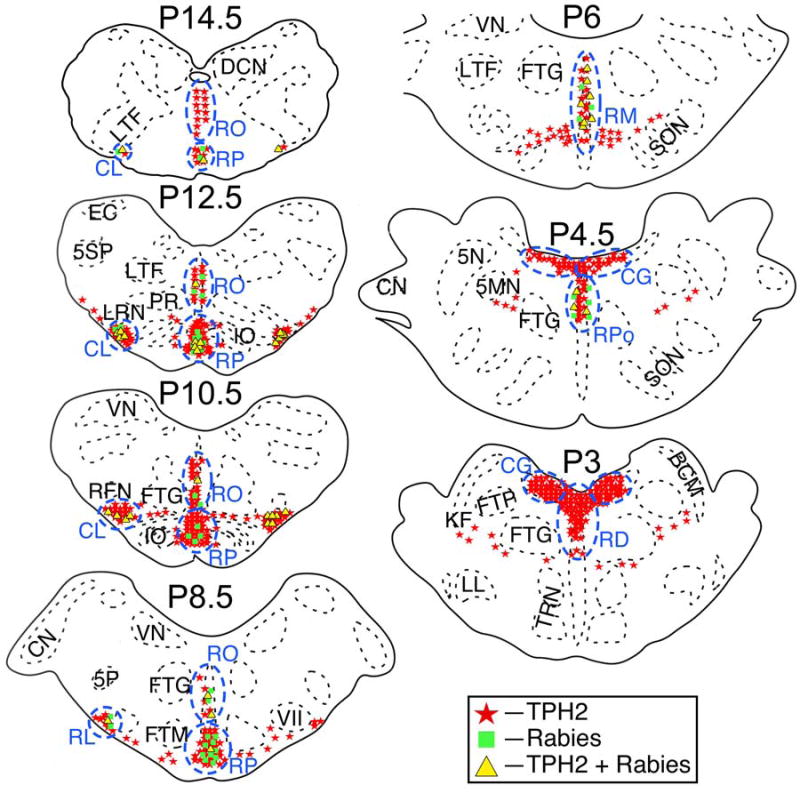
The locations in animal C38 of TPH2-immunopositive neurons, neurons in the same regions that were immunopositive for rabies virus, and neurons that contained both antigens. Areas where a high density of TPH2-immunopositive neurons were observed are designated by blue dashed lines and lettering. Cell locations are shown on standard sections generated through reference to Berman’s cat brainstem atlas (Berman, 1968). The location of each section relative to stereotaxic zero (P0) is indicated. Abbreviations: 5MN, trigeminal motor nucleus; 5N, trigeminal nucleus; 5P, parvocellular spinal trigeminal nucleus; 5SP, spinal trigeminal nucleus; BCM, marginal nucleus of brachium conjunctivum; CG, central gray; CL, caudal ventrolateral serotoninergic region; CN, cochlear nuclei; DCN, dorsal column nuclei; EC, external cuneate nucleus; FTG, gigantocellular tegmental field; FTM, magnocellular tegmental field; FTP, pontine tegmental field; IO, inferior olivary nucleus; KF, Kölliker-Fuse nucleus; LL, nucleus of the lateral lemniscus; LRN, lateral reticular nucleus; LTF, lateral tegmental field; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; PR, paramedian reticular nucleus; RD, raphe dorsalis; RFN, retrofacial nucleus; RL, rostral ventrolateral serotoninergic region; RM, raphe magnus; RO, raphe obscurus; RP, raphe pallidus; RPo, pontine raphe nuclei; SON, superior olivary nucleus; TRN, tegmental reticular nucleus; VII, facial nucleus; VN, vestibular nuclei.
