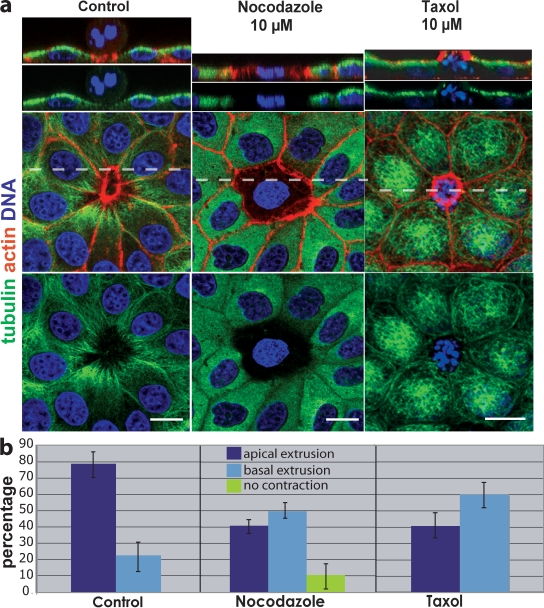
Figure 4.
Disruption of microtubules alters the direction a cell extrudes. (a) In control (DMSO-treated) MDCK monolayers, microtubules dip down toward the basolateral surface of the actin ring, whereas nocodazole either blocks contraction of the ring (as shown) or drives extrusion basally. Stabilizing microtubules with taxol freezes microtubules at the apex compared with control and drives extrusion basally. Broken lines indicate the site of cross sections from 3D confocal reconstructions above. Bars, 10 µm. (b) Quantification of drug-treatments from six experiments, n = 1,350 extruding cells per treatment. P-values for apical and basal extrusions, respectively, were 0.0011 and 0.0066 for nocodazole and 0.0023 and 0.0023 for taxol. Error bars indicate SEM.