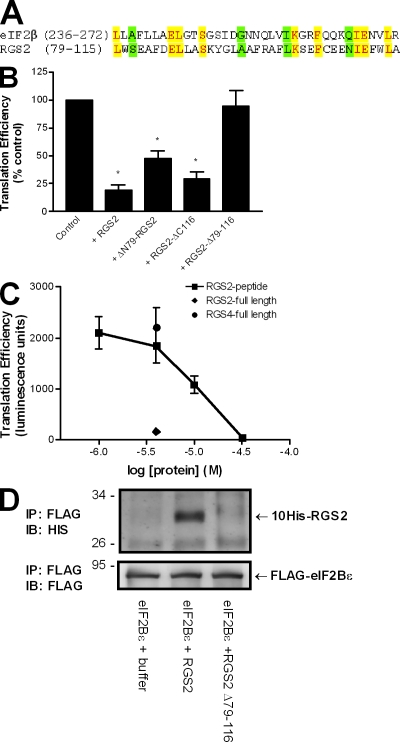
Figure 4.
RGS2-mediated inhibition of protein synthesis and binding to eIF2Bϵ is dependent on amino acids 79–116. (A) Comparison between the putative eIF2Bϵ-interacting domain of RGS2 and the established eIF2Bϵ-interacting domain of eIF2β. Identical residues are denoted by yellow shading, whereas conserved substitutions are indicated in green. (B) The effect of full-length RGS2, ΔN79-RGS2, RGS2-ΔC116, and RGS2-Δ79–116 (4 µM) was examined on luciferase protein synthesis in a reticulocyte-based in vitro translation assay as described in Materials and methods. The data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.05 versus control (one-sample t test). (C) The effect of RGS2, RGS4, or an RGS2 peptide corresponding to amino acid residues 79–116 on luciferase protein synthesis. The data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. (D) RGS2 and RGS2-Δ79–116 were examined for interactions with monomeric eIF2Bϵ as described for Fig. 1. The blots are representative of three independent experiments. IB, immunoblot. Molecular mass indicators are expressed in kilodaltons.