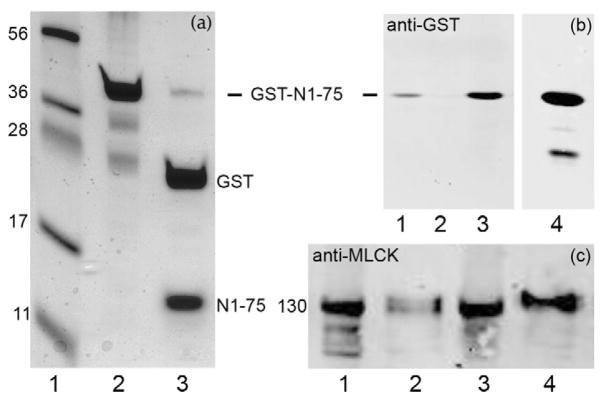
FIGURE 6. Characterization of expressed actin-binding domain of MLCK (GST-N1-75MLCK).
(a), SDS-PAGE with Coomassie Blue staining. Lane 1, markers (numbers at left indicate kDa); lane 2, purified GST-N1-75MLCK (abbrev. N1-75); lane 3, thrombin digest of GST-N1-75MLCK producing GST and N1-75MLCK. (b), Western blot analysis (anti-GST) demonstrating binding of GST-N1-75MLCK to myofilaments. Lane 1, myofilaments were incubated with 100 μM GST-N1-75MLCK in 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 80 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT and centrifuged to pellet the myofilaments and bound proteins; lane 2, myofilaments were treated with 50 mM MgCl2 to remove endogenous MLCK; lane 3, myofilaments treated with 50 mM MgCl2 then GST-N1-75 MLCK (note increased binding of GST-N1-75MLCK); lane 4, purified GST-N1-75MLCK. (c), Myofilaments were stirred for 10 min with 0.5 ml of 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 80 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT without or with 100 μM GST-N1-75MLCK and centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 30 min. Pellets were resuspended in 0.5 ml buffer. Lanes 1 (pellet) and 2 (supernatant): incubated without GST-N1-75MLCK; lanes 3 (pellet) and 4 (supernatant): myofilaments were extracted with GST-N1-75MLCK. Results represent n = 3–5. GST-N1-75MLCK treatment dissociates ~ ½ of the MLCK under these conditions.