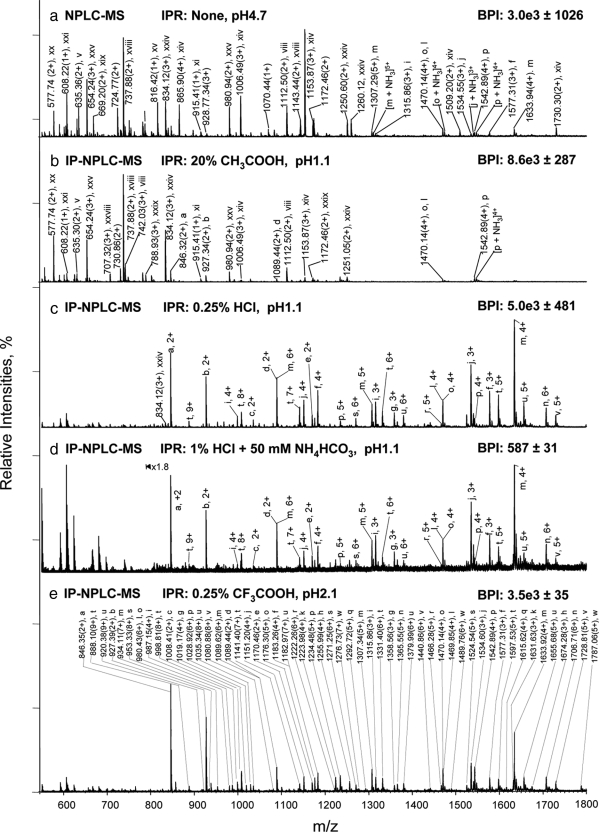
Fig. 1.
Isolation of glycopeptides from a RNase B and fetuin tryptic digest using IP-NPLC. Total ion mass spectrum from NPLC-ESI-MS of peptides in the glycopeptide fraction from the tryptic digest injected with the following ion-pairing reagents (IPR): a, none in 80% ACN/20% H2O; (pH 4.7); b, 20% acetic acid in 80% ACN (pH 1.1); c, 0.25% HCl in 80% ACN/20% H2O (pH 1.1); d, 50 mm NH4HCO3 + 1% HCl in 80% ACN/20% H2O (pH 1.1); and e, 0.25% TFA in 85% ACN/15% H2O (pH 2.1). BPI, base peak intensities. Throughout this report, the total ion mass spectrum for NPLC-ESI-MS of the glycopeptide fraction refers to the summed MS scans across the NPLC retention times between the most hydrophobic high mannose type glycopeptide (a) from RNase B (6.5–9.0 min depending on the ion-pairing reagents used (Fig. 2, 2nd top panel) and the most hydrophilic sialylated glycopeptide from fetuin detected (earlier than 13 min). Non-glycopeptides eluted earlier than the high mannose type glycopeptide (a) of RNase B when HCl or TFA were used as ion-pairing reagents. The tryptic digest contains 14.2 pmol of RNase B tryptic digest + 13.8 pmol of fetuin tryptic digest. The solvent compositions used to dissolve the different IPR, CH3COOH, HCl, and TFA with/without NH4HCO3 are as indicated in each panel of the figure. The pH values listed are those of the samples. All abundant ions that are not labeled in Fig. 1 are singly charged contaminants.