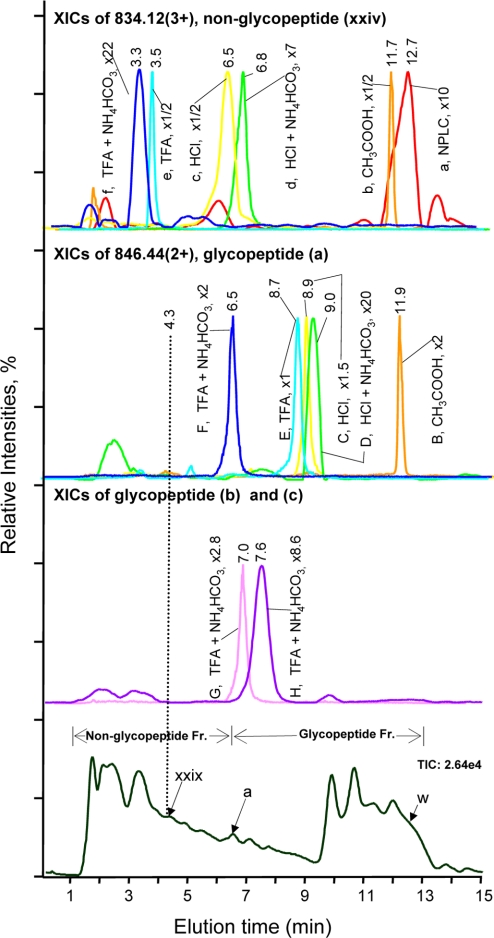
Fig. 2.
Effect of acids as ion-pairing reagents on peptide retention in IP-NPLC. Top panel, overlaid extracted ion chromatograms (XICs) of m/z 834.12 (3+) of the hydrophilic non-glycopeptide (xxiv), CKPVNTFVHESLADVQAVCSQK, from the RNase B and fetuin tryptic digest injected with the following ion-pairing reagents (IPR): (a) none; (b) 20% CH3COOH; (c) 0.25% HCl; (d) 1% HCl + 50 mm NH4HCO3; (e) 0.25% TFA; and (f) 1% TFA + 50 mm NH4HCO3. Second top panel, overlaid XICs of m/z 846.44 (2+) of the least hydrophilic glycopeptide (a), NLTK-GlcNAc2Man5, from the same tryptic digest injected with the following IPRs: (B) 20% CH3COOH; (C) 0.25% HCl; (D) 1%HCl + 50 mm NH4HCO3; (E) 0.25% TFA; and (F) 1% TFA + 50 mm NH4HCO3; Second bottom panel, (G) XIC of m/z 927.48 (2+) of the glycopeptide (b), NLTK-GlcNAc2Man6; (H) XIC of m/z 1008.43 (2+) of the glycopeptide (c), NLTK-GlcNAc2Man7. IPR used for G and H: 1% TFA + 50 mm NH4HCO3. Bottom panel, total ion chromatogram from IP-NPLC-ESI-MS of the standard tryptic digest injected with 1% TFA + 50 mm NH4HCO3. The magnification factors (e.g. x1) of the base peak intensity (BPI) of the extracted ions were relative to the BPI of (E) for normalization. The elution time of the least hydrophilic tryptic glycopeptide (a) of RNase B, i.e. the reference time determining the starting elution time of glycopeptide fraction, varies from 6.5 min to 11.9 min depending on the IPR used (Second top panel). The broken line at 4.3 min indicates the elution time of the most hydrophilic tryptic non-glycopeptide (xxix) present in the sample. w, glycopeptide (w) in Table II; Fr., fraction.