Figure 7.
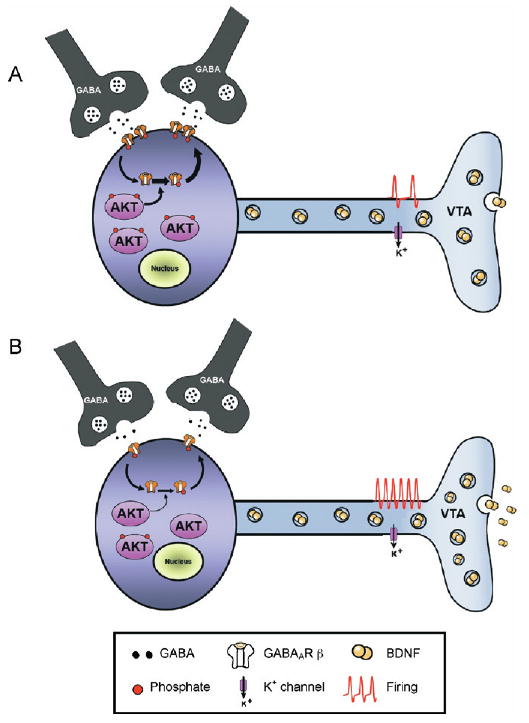
Working model of the role of thymoma viral proto-oncogene (AKT) in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) after chronic stress. (A) At baseline, VTA dopamine neurons receive tonic inhibition from surrounding GABAergic interneurons as well as projection neurons. High basal levels of AKT activation support the membrane insertion of GABAA receptors (GABAAR) via the AKT-medi-ated phosphorylation of GABAAR β2 subunits. (B) Following chronic exposure to social defeat stress, reduced AKT tone leads to reduced GABAergic transmission, through a combination of reduced GABAAR membrane expression and reduced GABA release. This leads to enhanced excitability and subsequent increased rates of activity-dependent BDNF release in nucleus accumbens. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GABA, γ-amino butyric acid.
