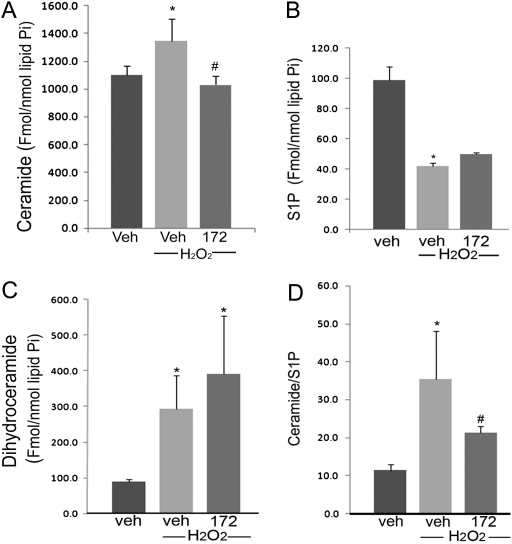
Figure 3.
Effect of CFTR inhibitors on intracellular sphingolipid levels in lung endothelial cells. (A–C) Ceramide, S1P, and dihydroceramide levels were measured by tandem mass spectrometry in primary human lung microvascular endothelial cells treated with H2O2 (250 μM, 6 h) in the presence of the CFTR inhibitor CFTRinh-172 (20 μM). Sphingolipid levels were normalized by intracellular phospholipids (inorganic phosphorus content, Pi) and plotted as mean ± SEM (n = 3; *P < 0.05 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus H2O2). (D) The ratio of ceramide/S1P in lung endothelial cells, an indicator of pro-apoptotic/anti-apoptotic intracellular balance, was calculated from the values measured in A and B (mean ± SEM; n = 3; *P < 0.05 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus H2O2 treatment).