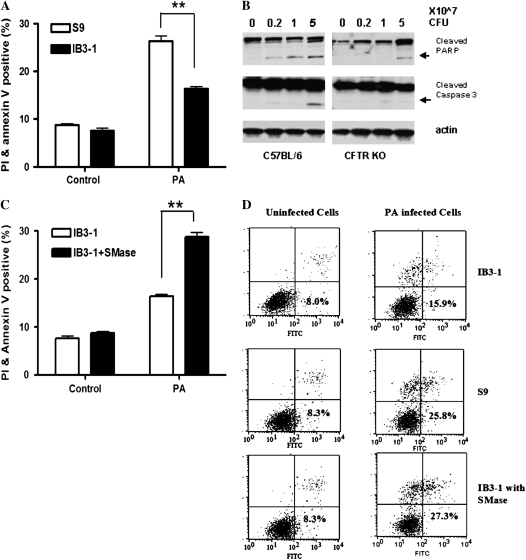
Figure 6.
Decreased apoptotic response to P. aeruginosa (PA) infection in CF is associated with defective ASMase activity. (A) Defective apoptotic/necrotic response in CF bronchial epithelial cells. IB3-1 and S9 cells were infected with PAO1 (50 cfu/cell) for 5 hours. Apoptotic/necrotic responses were analyzed by fluorescein isothiocyanate–labeled Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) staining flow cytometry assay (n = 4, **P < 0.0001). (B) Decreased apoptotic response to PA infection in CFTR KO mice. CFTR KO (Cftrtm1Unc-TgN(FABPCFTR)) mice and C57BL/6 mice were either uninfected or infected with various doses (2 × 106, 1 × 107, and 5 × 107 cfu) of PAO1 for 6 hours. The lung homogenates were collected to analyze Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and caspase 3 protein levels by Western blot. (C) Exogenous bacteria SMase increased apoptotic/necrotic responses with PAO1 infection in CF bronchial epithelial cells. Exogenous bacteria SMase (0.03 U/ml) from Staphylococcus aureus was added to IB3-1 cells 1 hour before PA infection. Apoptotic/necrotic responses were analyzed by Annexin V and PI staining flow cytometry assay (n = 4, **P < 0.0001). (D) Annexin V and PI staining flow cytometry assay results. Treatments of IB3-1 cells and S9 cells were mentioned as above. Annexin V and PI values for each treatment were plotted on the x axis and y axis, respectively. Shown are % cells of each treatment group in top left, top right, and bottom right quadrants (Annexin V+ and/or PI +). Data represent four independent experiments.