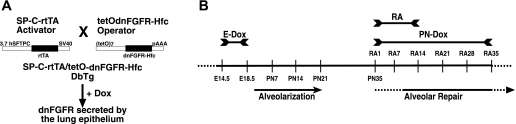
Fig. 1.
A: schematic drawing of the mouse breeding to generate double transgenic (DbTg) mice. Heterocygote mice of the activator line, SP-C-rtTA line 1, are crossed to heterocygote mice of the operator line, tetOdnFGFR-Hfc. According to Mendelian inheritance, only 25% of the offspring carry both transgenes, DbTg mice. Only in DbTg progenies doxycycline (dox) treatment activates dominant-negative FGF receptor (dnFGFR) expression specifically in the lung epithelium (20). B: timeline of dox and retinoic acid (RA) treatment to induce alveolar simplification and alveolar repair, respectively, in DbTg mice. Dox treatment from embryonic day 14.5 (E14.5) to E18.5 (E-Dox) induces expression of dnFGFR and inhibits postnatal alveolarization. RA treatment from postnatal day 35 (PN35) to PN48 induces alveolar repair. Postnatal dox treatment from PN35 throughout RA treatment (PN-Dox) induces dnFGFR expression and inhibits alveolar repair. Alveolar repair in the presence and absence of FGF signaling was assessed in DbTg mice after embryonic inhibition of FGF signaling 7, 14, 21, 28, and 35 days after initiation of RA treatment (RA7, RA14, RA21, RA28, and RA35). SV40, simian virus 40.