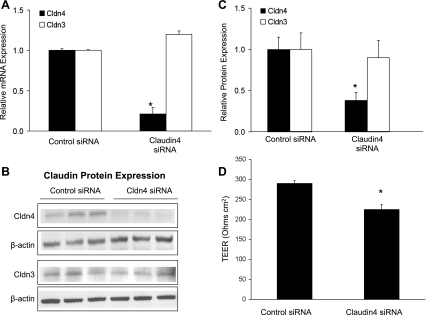
Fig. 5.
Claudin-4 knockdown with small interfering RNA (siRNA). To extend and confirm the CPEBD studies by specifically blocking only claudin-4 expression, primary human type II-like distal lung epithelial cells (DLECs) were transfected with siRNA targeted to claudin-4. A: at 72 h posttransfection, claudin-4 siRNA (20 nM) decreased claudin-4 mRNA abundance without affecting claudin-3 expression (*P < 0.05 compared with nonsilencing control siRNA without homology to any known human gene; n = minimum of 3 replicates of 6 wells each, means ± SE). B: claudin-4 siRNA significantly decreased claudin-4 but not claudin-3 protein expression. C: densitometry of Western blot data normalized to β-actin showed a significant decrease in claudin-4 protein with targeted siRNA (n = 3 per group; P < 0.05; means ± SD) but no change in claudin-3 protein levels. D: claudin-4 knockdown decreased transepithelial electrical resistance in human cells with an effect size comparable with CPEBD (*P < 0.05 compared with nonsilencing control siRNA; n = minimum of 3 replicates of 6 wells each, means ± SE). These data support the hypothesis that claudin-4 expression increases transepithelial resistance and decreases paracellular ion transport.